6 Easy Steps To Configure SNMP on Redhat Linux or CentOS
The other day I was working on adding some of the Redhat servers in to production for monitoring. I also got the SNMP community string from the team who is managing the monitoring tools as well.
I was so confident that I even informed them that I would configure the SNMP on the server in another 5 mins :).
Do you know what happened when I logged into the server and went to edit the SNMP config file?
1 | /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf |
It turns out that “snmpd.conf” file doesn’t exist, oh man…
I went ahead and checked on another server I had added earlier to the production, and the SNMP configs were present on that server.
Since the SNMP file doesn’t exist on the server, I concluded that the SNMP package not installed on my current RedHat server, and I decided to download and install them.
I made sure I have internet access on this box and I tried to download the SNMP package by running the command below, which would download all the required dependencies to run the SNMP service on the server.
However, I got the below error message.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | [root@GetLabsDone ~]# yum install -y net-snmp net-snmp-libs net-snmp-utilsLoaded plugins: langpacks, product-id, search-disabled-repos, subscription-managerThis system is not registered with an entitlement server. You can use subscription-manager to register.There are no enabled repos. Run "yum repolist all" to see the repos you have. To enable Red Hat Subscription Management repositories: subscription-manager repos --enable To enable custom repositories: yum-config-manager --enable |
Which means I don’t have a Redhat subscription!
Well, that can’t be happening, I already have Redhat subscription, and I shouldn’t be getting the above error message. Let’s go ahead and fix it.
So in this blog, I am going to cover how to configure SNMP on the Redhat and Centos machine. And we should be configuring the SNMP version 2.
After which is done you will have full visibility on your Redhat/Centos Linux server in production. I will also cover some troubleshooting steps when SNMP doesn’t work
How to add Redhat subscription to the server?
If you are a Centos user you may skip this step and go right into the SNMP installation and configuration here.
Since the error indicated that I don’t have Redhat subscription, I then went ahead and checked the Redhat subscription status by entering the commands below.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | [root@getlabsdone ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/rhn/systemid cat: /etc/sysconfig/rhn/systemid: No such file or directory [root@getlabsdone ~] # sudo subscription-manager status+-------------------------------------------+ System Status Details+-------------------------------------------+Overall Status: Unknown |
The output basically shows that I hadn’t added this server to the Redhat subscription.
I had license to add this server to the subscription. Hence, I went ahead and added the subscription by running the below command.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | [root@getlabsdone ~]# subscription-manager register --auto-attachRegistering to: subscription.rhsm.redhat.com:443/subscriptionUsername: your usernamePassword: your passwordThe system has been registered with ID: you will find your ID hereInstalled Product Current Status:Product Name: Red Hat Enterprise Linux ServerStatus: Subscribed |
Let me check the Redhat subscription status now.
1 2 3 4 5 | [root@getlabsdone ~]# sudo subscription-manager status+-------------------------------------------+System Status Details+-------------------------------------------+Overall Status: Current |
aha! some sigh of relief as I just added the Redhat server to the Redhat subscription now.
Note: Can you run this command while the server is in production?.
Of course, you can as it’s just attaching the subscription and won’t make any further changes on the server.
What if I have a test environment where I don’t have Redhat subscription?
If you are in the lab it’s very important that you enable ‘Remote Management for Linux’ during the Redhat OS installation. That way the server would enable the SNMP package before the installation and you would have the package ready to use. If not, you would need to attach the Redhat subscription to download the SNMP package to the system, which usually you may not have on lab servers. or you may need to find alternate ways to download and install the SNMP package on the Redhat server later on.

Why do we need SNMP?
The SNMP protocol helps you to monitor Redhat / Centos servers or any other network hosts on the network. With the help of the SNMP protocol, the monitoring tools can show you many device performance parameters. Such as CPU utilization based on each core, memory utilization, hard disk utilization, network interface utilization, and so on.
How to configure SNMP on redhat linux or Centos ?
The below are the steps that we are going to use to configure SNMP Linux.
These steps are same for both Redhat and CentOS versions.
One great thing about CentOS is that you don’t need to have any sort of subscription as it’s community-based.
- Installation of SNMP linux package.
- SNMP configuration in Redhat and CentOS.
- Add SNMP service at the startup.
- Restart the SNMP service
- Allow SNMP port on Linux firewall.
Step 1. Installation of SNMP linux package.
- After you have added the subscription to the Redhat server, you can go ahead and install the SNMP files by running the below command.
Note: To install snmp on centos 7/8 you should use the same commands as well.
1 | [root@getlabsdone ~]# yum install -y net-snmp net-snmp-libs net-snmp-utils |
Eventually, you would be able to see the below message saying that the SNMP package installation has completed.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | Installed: net-snmp.x86_64 1:5.7.2-37.el7 net-snmp-utils.x86_64 1:5.7.2-37.el7Updated: net-snmp-libs.x86_64 1:5.7.2-37.el7Dependency Updated: net-snmp-agent-libs.x86_64 1:5.7.2-37.el7Complete! |
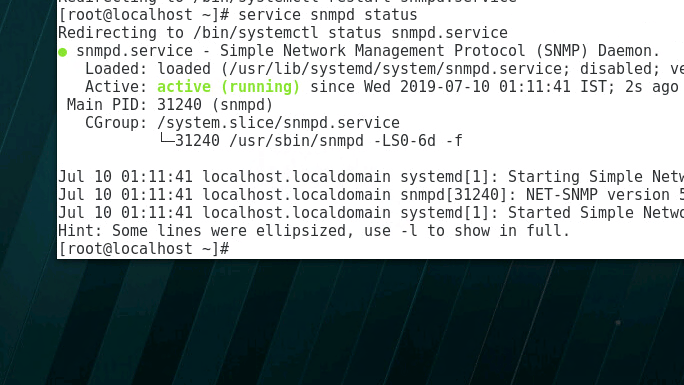
- You can check the status of SNMP on the server by running the below command.
1 2 3 4 5 | [root@getlabsdone ~]# service snmpd statusRedirecting to /bin/systemctl status snmpd.service● snmpd.service - Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Daemon. Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/snmpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: inactive (dead) |
As you can see the SNMP status is inactive at the moment. even though we have installed the package, we are going to fix that soon.
The steps mentioned here is same for Centos as well except the subscription.
Step 2. SNMP configuration in Redhat and CentOS.
Now that you have SNMP service installed on both Redhat or Centos server, next you would have to add the server to the SNMP monitoring.
to do that, you need to change the SNMP community string under /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf
- Let’s go ahead and edit the SNMP configuration file and add the string.
1 | vi /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf |
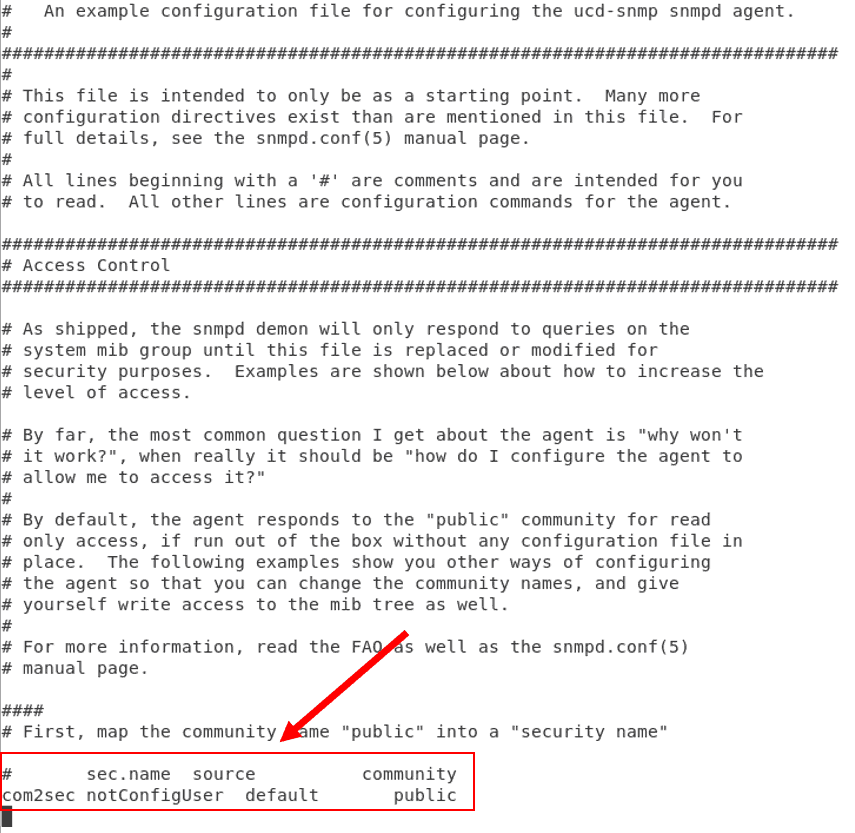
- Goto the below line and edit the string ‘public’ which is the default to whatever the community string you may have received from the team.
1 | com 2sec notConfigUser default public |
- Once you added the string to the config, save the configuration and restart the SNMP service using the below command.
1 2 3 | [root@getlabsdone admin]# service snmpd restartRedirecting to /bin/systemctl restart snmpd.service[root@getlabsdone admin] |
- SNMP service now restarted and it should be active now, you can check the status by the command
1 | service snmpd status |
Change the default SNMP configuration.
The configuration which we just made above is the default SNMP configuration and it should be fine for testing. however, if you are planning to set up SNMP in production you should use either rocommunity which is read-only community, or rwcommunity which is SNMP with read-write access.
You should also specify the monitoring server address or subnet to enhance the security.
- Open SNMP configuration again, and comment the SNMP public string

Then add the read-only community string along with the monitoring server IP address. My monitoring server IP address is 192.168.127.1.
so the configuration should look like this, As you can see I also changed the community string to a different one.
1 | rocommunity mysnmp1! 192.168.127.1 |
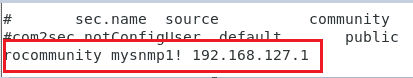
This way only the server with IP address 192.168.127.1 can poll the device through SNMP, the rest of the IPs will not be allowed.
After you modified the configuration restart the SNMP service as well.
For most of the deployments the read only community access should work.
If you require to have SNMP read-write access then you may change the configuration like below. And restart the SNMP service again.
1 | rwcommunity mysnmp1 192.168.127.1 |
Step 3. Add SNMP service at the startup.
After the SNMP restart, the service should be up and running. However you don’t want the SNMP service to be inactive every-time when the system reboots.
To avoid such situations, you can add the SNMP service to start everytime when the system boots by running the below commands.
1 | chkconfig snmpd on |
And you don’t have to manually start the SNMP service later on.
Step 4. Restart the SNMP service.
Sometimes your monitoring team may say that redhat snmp monitoring still not working even after it has configured. The problem could be either the SNMP service is not running or the SNMP port 161 not allowed on the Redhat or CentOS Linux server firewall or iptables.
Remember, on the step 1 when we installed the SNMP package, it was inactive. If the SNMP service is not running or if it is in inactive state you can type service SNMP startorrestart to activate the service.
Step 5. Allow SNMP port on Linux firewall.
Firewalld is the firewall service on Redhat 7 and CentOS 7.
If you running an older version than that, it uses IPtables. To see which version you are running enter the command cat /etc/redhat-release
- Check the status of firewall service on Rhel 7 or Centos 7.
For older version tryservice iptables status, basically replace firewalld with iptables.
by default firewall on the RedHat would be active, as you can see below.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | [root@getlabsdone ~]# service firewalld statusRedirecting to /bin/systemctl status firewalld.service● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Tue 2019-07-09 21:51:15 IST; 18h left Docs: man:firewalld(1) Main PID: 922 (firewalld) CGroup: /system.slice/firewalld.service └─922 /usr/bin/python -Es /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid |
There are two ways you can fix an issue with SNMP that doesn’t work.
a. Allowing SNMP via Firewalld.
- First, you can stop the firewall service on Redhat by issuing the below command to test. This should allow SNMP port 161 and snmp starts to work.
1 | service firewalld stop |
Note: Stopping the firewall service is not a recommended solution in the production environments. Only do this when you are in a non-production environment.
- Second, you can allow the SNMP port number 161 on the Redhat firewall.
To allow the SNMP port 161 on the Linux firewall you can type the below command to allow SNMP service on the system, that would enable the port as well.
1 2 3 | [root@getlabsdone ~]# firewall-cmd --add-service=snmp --permanent success[root@getlabsdone ~]# |
- And restart the firewall service.
1 2 3 | [root@getlabsdone ~]# service firewalld restartRedirecting to /bin/systemctl restart firewalld.service[root@getlabsdone ~]# |
b. Allow SNMP port on IPtables.
If you are using iptables instead of firewall you may enable the snmp port as below.
1 2 | # iptables -I INPUT -p udp -m udp --dport 161 -j ACCEPT# iptables -I INPUT -p udp -m udp --dport 162 -j ACCEPT |
And save the config
1 | # iptables-save > /etc/sysconfig/iptables |
Step 6. Test the SNMP configuration using SNMPWALK.
You are all set now to monitor the device, if you would like to test the configuration that you just made from your end, you can do so by running the snmpwalk command.
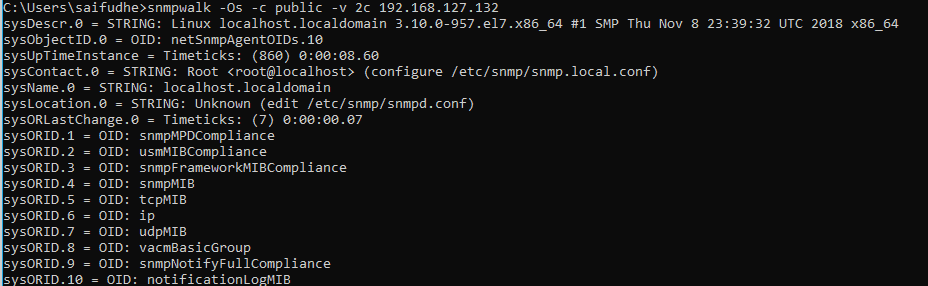
I am checking the SNMP configuration whether it is working or not when my string was ‘public’
1 | snmpwalk -Os -c public -v 2c 192.168.127.132 |
As you can see I am getting a response which means it is working now.
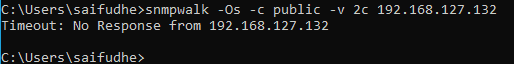
I re-ran the same command again after I changed the default SNMP community string ‘public’.
As you can see I am getting an error Time out: No response from the client.
Which is expected as I no longer use the community string public anymore.
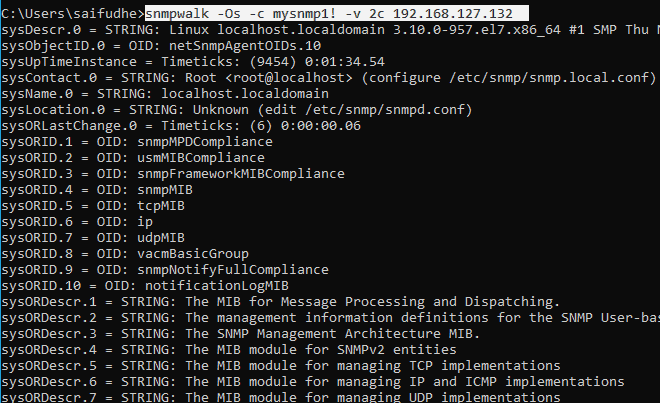
When I changed the community string to a new one mysnmp1!, and when I ran the command again, you can see that I am getting a response now through SNMPWALK
Always keep in mind the below points, whenever you make any changes to SNMP on linux.
- Make sure the SNMP service or port 161 and 162 are allowed on the firewall.
- Each time when you make changes restart the SNMP services.
- Make sure that you are using the right community string.
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar