How to Install LAMP Stack with PhpMyAdmin in Ubuntu 18.04
A LAMP stack is composed of packages such as Apache, MySQL/MariaDB and PHP installed on a Linux system environment for hosting websites and apps.
Read Also: Install Apache, MariaDB, PHP and PhpMyAdmin in Ubuntu 18.04
PhpMyAdmin is a free, open source, well known, fully-featured, and intuitive web-based frontend for administering MySQL and MariaDB database. It supports various database operations, and has many features that allow you to easily manage your databases from a web interface; such as importing and exporting data in various formats, generating complex and useful queries using Query-by-example (QBE), administering multiple servers, and much more.
Requirements:
- Minimal Ubuntu 18.04 server Installation.
- Access to server via SSH (if you don’t have direct access).
- Root user privileges or use sudo command to run all commands.
In this article, we will explain how to install LAMP stack with PhpMyAdmin in Ubuntu 18.04.
Step 1: Install Apache Web Server on Ubuntu 18.04
1. First start by updating your software packages and then install Apache web server using following commands.
2. After the installation process is complete, the apache service should start automatically and will be enabled to start at system boot time, you can check if it’s up and running using following command.
3. If you have a system firewall enabled and running, you need to open the ports 80 and 443 to allow client connection requests to apache web server via HTTP and HTTPS respectively, then reload the firewall settings as shown.
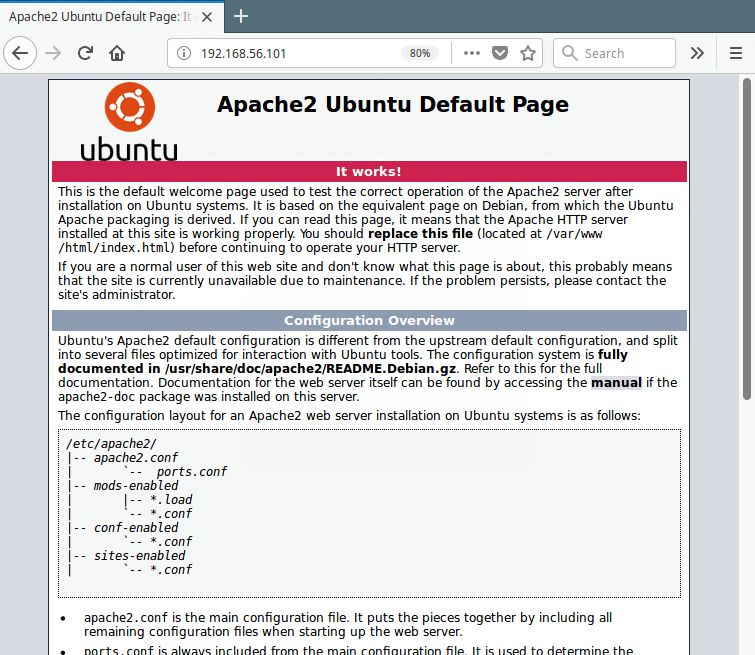
4. Now verify your Apache installation by testing default test page at the below URL from a web browser.
If you see the apache default web page, it means your installation is working fine.
Step 2: Install MariaDB on Ubuntu 18.04
5. Now install MariaDB, is a free, open source database management system forked from MySQL and it is a community developed project being led by the original developers of MySQL.
6. The MariaDB services should start automatically after installation, check its status to ensure that it is up and running.
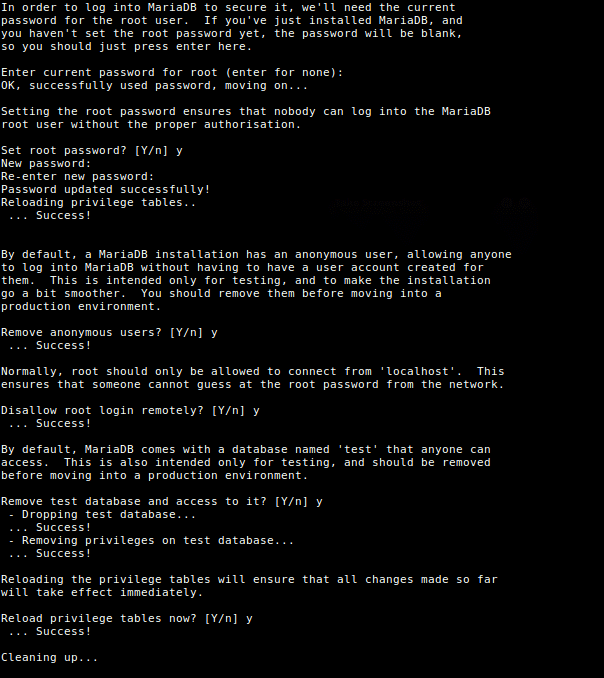
7. The MariaDB installation is not secure by default, you need to execute a security script that comes with the package. You will be asked to set a root password to ensure that nobody can log into the MariaDB.
Once you execute the script, it will ask you to enter current password for root (enter for none):
Then enter yes/y to the following security questions:
- Set root password? [Y/n]:
y - Remove anonymous users? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) :
y - Disallow root login remotely? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) :
y - Remove test database and access to it? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) :
y - Reload privilege tables now? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) :
y
Step 3: Install PHP on Ubuntu 18.04
8. PHP is one of the most widely used server side scripting language used to generate dynamic content on websites and apps. You can install PHP (default version is PHP 7.2) and other modules for web deployments using following command.
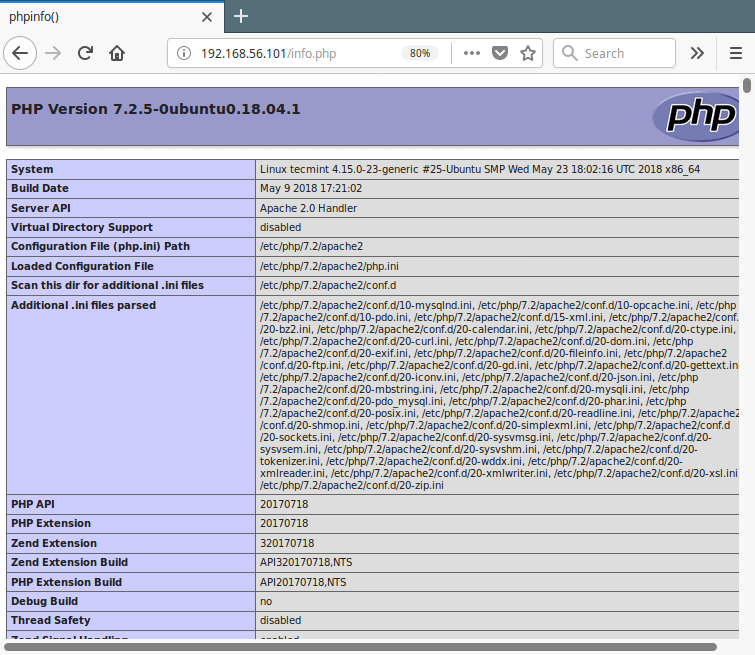
9. Once PHP installed, you can test your PHP setup by creating a simple info.php page in your web server document root, using this single command.
10. Then open a web browser, and enter this URL to view the php information page.
Step 4: Install PhpMyAdmin on Ubuntu 18.04
11. Finally, you can install phpMyAdmin for administrating MySQL/MariaDB databases from the comfort of a web browser, by running following command.
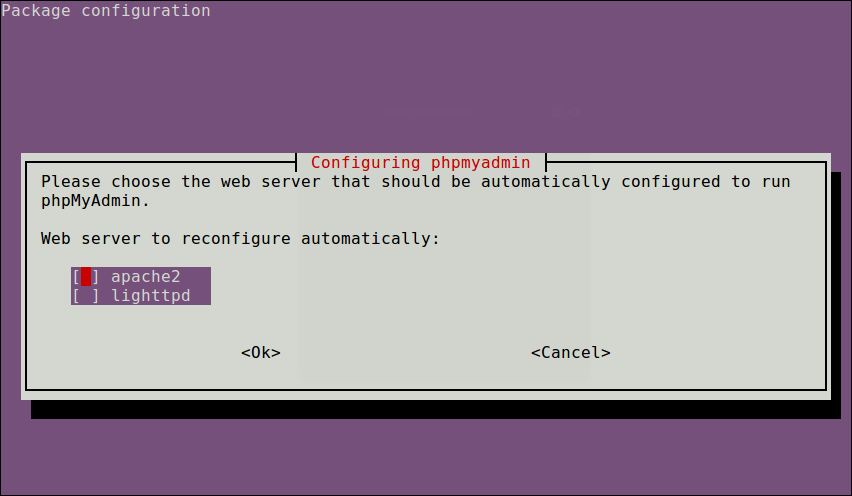
Through the package installation process, you will be asked to choose the web server that should be automatically configured to run phpMyAdmin, select apache by pressing the space bar and press Enter.
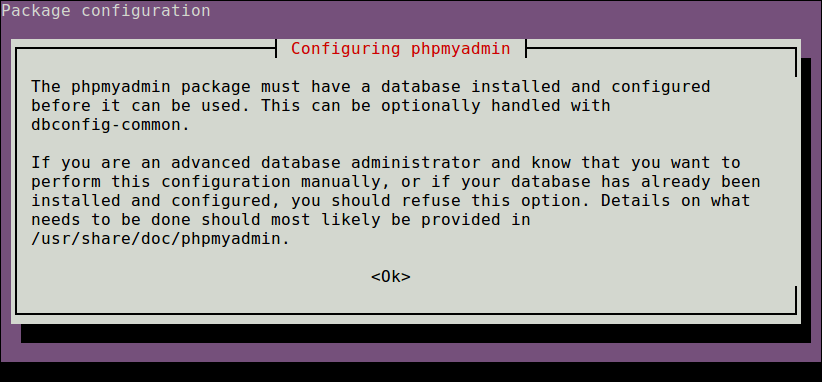
12. Next, enter the password for the MySQL/MariaDB administrative user so the installer can create database for phpmyadmin.
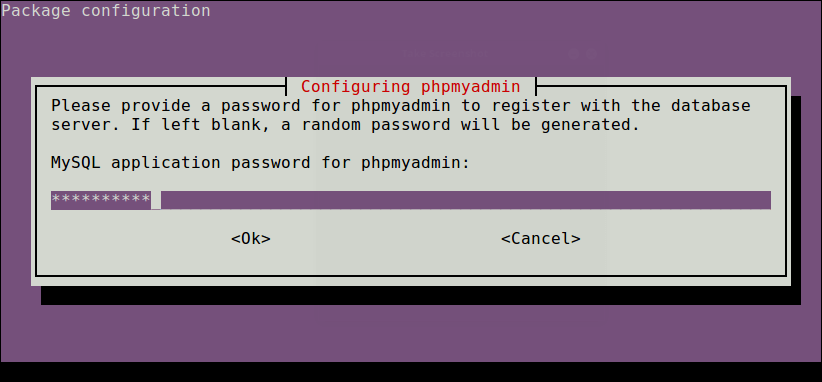
13. Once everything installed, you can now restart the apache2 service to effect the recent changes.
Note: If the PhpMyAdmin package has not been enable to work with apache web server automatically, run the following commands to copy the phpmyadmin apache configuration file located under /etc/phpmyadmin/ to apache webserver available configurations directory /etc/apache2/conf-available/ and then activate it using the a2enconf utility, and restart apache service effect the recent changes, as follows.
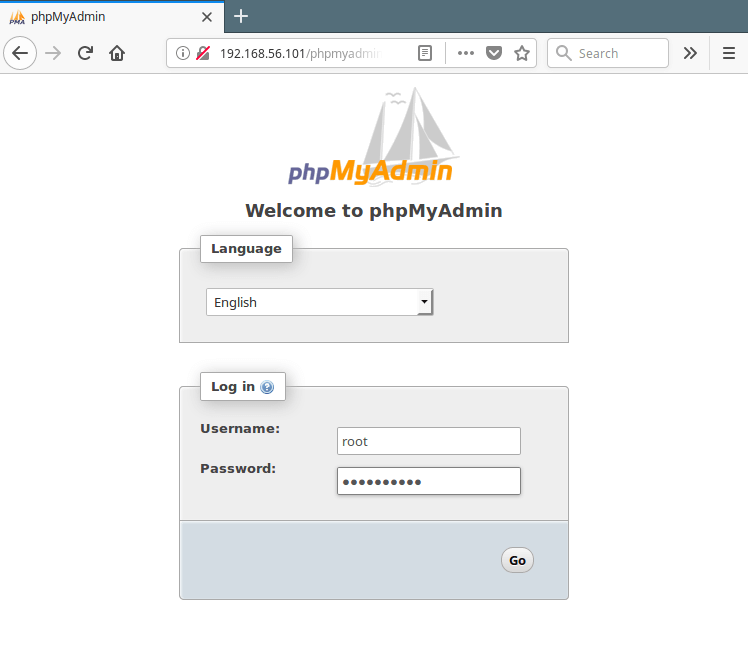
14. Lastly, from a web browser, and type the following URL to access you phpMyAdmin web frontend.
Use the root credentials to authenticate in the phpMyAdmin, as shown in the following screen shot.
Important: Starting from MySQL 5.7, root login requires sudo command, therefore the root login will fail via phpmyadmin, you may need to create another admin user account. Access the mariadb shell using the root account from a terminal, and run the following commands to create a new user:
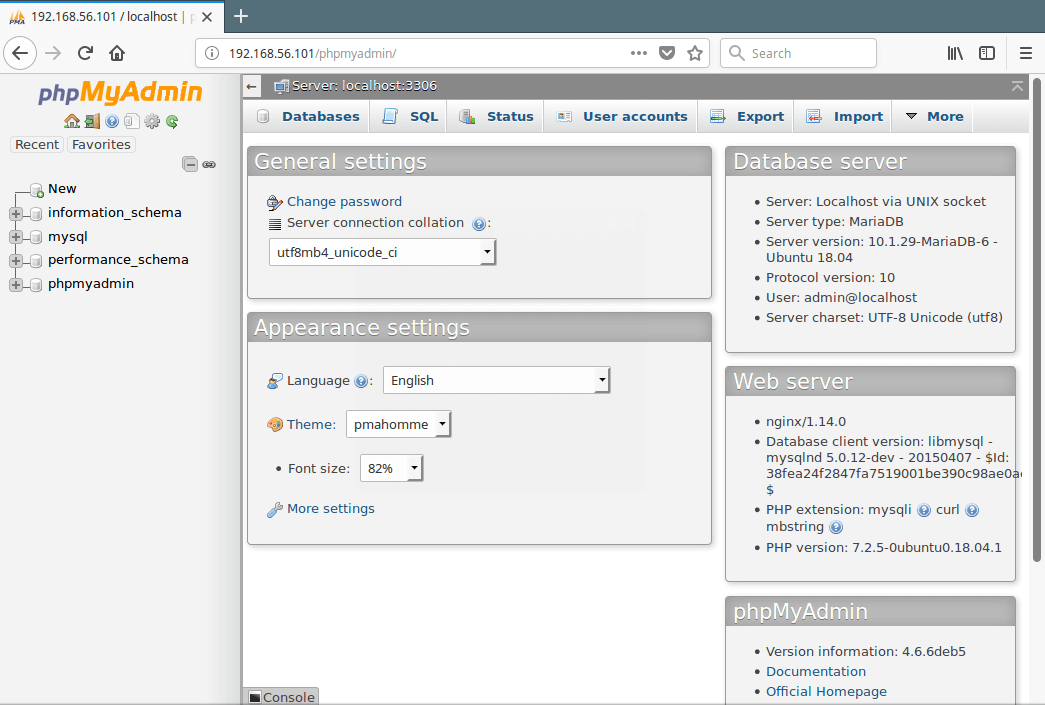
Now log into PhpMyAdmin using the new admin credentials to administer your databases.
To secure your PhpMyAdmin web interface, check this article: 4 Useful Tips to Secure PhpMyAdmin Web Interface.
That’s it! In this article, we have explained how to setup LAMP stack with the latest PhpMyAdmin in Ubuntu 18.04. Use the comment form below to send us your queries, or thoughts about this guide.
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar