Install Magento 2.x on Ubuntu 18.04 with Nginx, MariaDB, PHP 7.1 — Programming School
This is just a small explanation about install magento 2.x on ubuntu 18.04. For full article please go through THIS article. Thank You.
Install Magento 2.x on Ubuntu 18.04 with Nginx, MariaDB, PHP 7.1:
This article shows how anyone can install Magento 2.x on Ubuntu 18.04 with Nginx, MariaDB and PHP 7.1. (LEMP)
Also, Magento is PHP 7.1 compatible… so why not use the latest PHP? However, before using PHP 7.1, make sure all your plugins and themes are compatible or you’ll seriously run into issues.
NOTE: IT IS NOT COMPATIBLE WITH PHP 7.2
STEP 1: INSTALL NGINX
Nginx HTTP Server represents the E in the LEMP stack… It’s probably the second most popular web server in use… so install it, since Magento needs it.
To install Nginx HTTP on Ubuntu server, run the commands below…
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nginx
After installing Nginx, the commands below can be used to stop, start and enable Nginx service to always start up with the server boots.
sudo systemctl stop nginx.service
sudo systemctl start nginx.service
sudo systemctl enable nginx.service
To test Nginx setup, open your browser and browse to the server hostname or IP address and you should see Nginx default test page as shown below. When you see that, then Nginx is working as expected.
Step 2: Install MariaDB Database Server
MariaDB database server is a great place to start when looking at open source database servers to use with Magento… To install MariaDB run the commands below…
sudo apt-get install mariadb-server mariadb-client
After installing MariaDB, the commands below can be used to stop, start and enable MariaDB service to always start up when the server boots..
Run these on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS
sudo systemctl stop mysql.service
sudo systemctl start mysql.service
sudo systemctl enable mysql.service
Run these on Ubuntu 17.10 and 18.04 LTS
sudo systemctl stop mariadb.service
sudo systemctl start mariadb.service
sudo systemctl enable mariadb.service
After that, run the commands below to secure MariaDB server by creating a root password and disallowing remote root access.
sudo mysql_secure_installation
When prompted, answer the questions below by following the guide.
- Enter current password for root (enter for none): Just press the Enter
- Set root password? [Y/n]: Y
- New password: Enter password
- Re-enter new password: Repeat password
- Remove anonymous users? [Y/n]: Y
- Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n]: Y
- Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n]: Y
- Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n]: Y
Restart MariaDB server
To test if MariaDB is installed, type the commands below to logon to MariaDB server
sudo mysql -u root -p
Then type the password you created above to sign on… if successful, you should see MariaDB welcome message
Step 3: Install PHP 7.1-FPM And Related Modules
PHP 7.1 may not be available on Ubuntu default repositories… in order to install it, you will have to get it from third-party repositories.
Run the commands below to add the below third party repository to upgrade to PHP 7.1
sudo apt-get install software-properties-common
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ondrej/php
Then update and upgrade to PHP 7.1-FPM
sudo apt update
Next, run the commands below to install PHP 7.1-FPM and related modules.
sudo apt install php7.1-fpm php7.1-common php7.1-mbstring php7.1-xmlrpc php7.1-soap php7.1-gd php7.1-xml php7.1-intl php7.1-mysql php7.1-cli php7.1-zip php7.1-curl php7.1-mcrypt
After installing PHP 7.2, run the commands below to open PHP default config file for Nginx…
sudo nano /etc/php/7.1/fpm/php.ini
Then make the changes on the following lines below in the file and save. The value below are great settings to apply in your environments.
file_uploads = On
allow_url_fopen = On
memory_limit = 256M
upload_max_filesize = 100M
max_execution_time = 360
cgi.fix_pathinfo = 0
date.timezone = America/Chicago
After making the change above, save the file and close out.
Step 4: Restart Nginx
After installing PHP and related modules, all you have to do is restart Nginx to reload PHP configurations…
To restart Nginx, run the commands below
sudo systemctl restart nginx.serviceStep 5: Create Magento Database
Now that you’ve installed all the packages that are required for Magento to function, continue below to start configuring the servers. First run the commands below to create a blank Magento database.
To logon to MariaDB database server, run the commands below.
sudo mysql -u root -p
Then create a database called magento
CREATE DATABASE magento;
Create a database user called magentouser with new password
CREATE USER 'magentouser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'new_password_here';
Then grant the user full access to the database.
GRANT ALL ON magento.* TO 'magentouser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'user_password_here' WITH GRANT OPTION;
Finally, save your changes and exit.
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT;
Step 6: Download Magento Latest Release
Next, visit Magento site and register for a free account. You must register before you’re allowed to download a copy. The community edition is what you’ll want to download.
After downloading, run the commands below to extract the download file into Nginx root directory.
sudo mkdir /var/www/html/magento/
sudo tar -zxvf ~/Downloads/Magento-CE*.tar.gz -C /var/www/html/magento/
Then run the commands below to set the correct permissions for Magento to function properly.
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/magento/
sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/html/magento/
Step 7: Configure Nginx Magento Site
Finally, configure Nginx configuration file for Magento. This file will control how users access Magento content. Run the commands below to create a new configuration file called magento
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/magento
Then copy and paste the content below into the file and save it. Replace the highlighted line with your own domain name and directory root location.
upstream fastcgi_backend { server unix:/run/php/php7.1-fpm.sock; }server { listen 80; listen [::]:80; index index.php index.html index.htm; server_name dev.magento.com; client_max_body_size 100M; set $MAGE_ROOT /chirag/worksace/magento; set $MAGE_MODE developer; include /var/www/html/magento/nginx.conf.sample; }
Save the file and exit.
Step 8: Enable The Magento Site
After configuring the VirtualHost above, enable it by running the commands below, then restart Nginx server…
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/magento /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/STEP 9: Check Our Magento Website

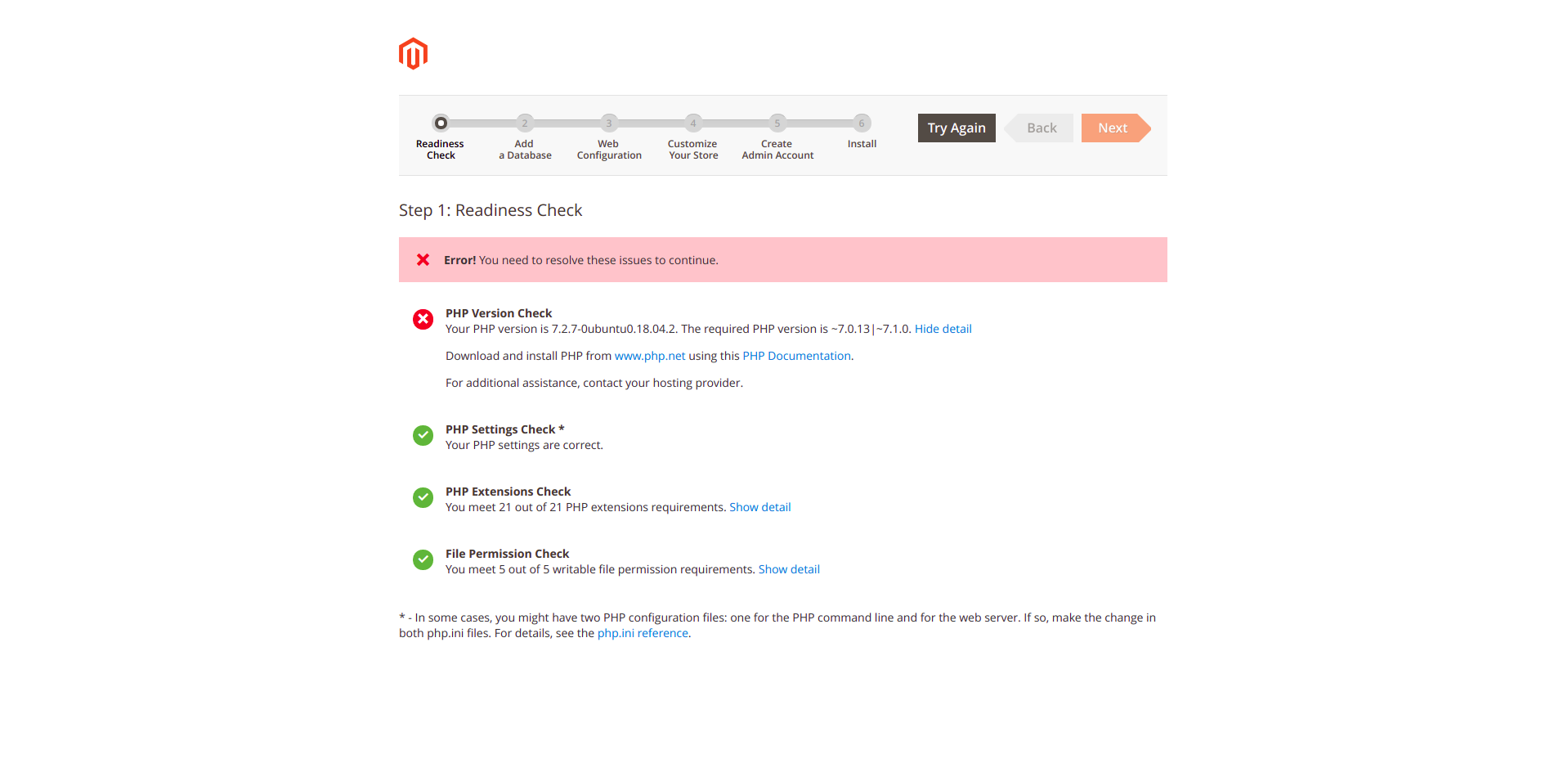
Next Step,

Next,

Congratulations! You’ve successfully installed Magento.
Happy Coding.

Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar