How to Setup Remote Desktop Connection Broker Load Balancing in Windows Server 2016
Summary of Steps
Accessing the RD Session Host Farm from an external network (e.g., the internet) can be done through the use of the Remote Desktop Gateway. This will be discussed in another tutorial.
This tutorial requires that Remote Desktop Services for Windows 2016 be already installed. It will show how to add an additional RD Session Host server to the RD Session Host Farm.
The following is the list of steps required to set up load balancing between the RD Session Host servers.
Plan the Installation and Setup Remote Desktop Services
You will need to plan what servers will have the necessary roles to be installed.
We need servers for the following roles:
- Remote Desktop Web Access
- Remote Desktop Gateway
- Remote Desktop Connection Broker
- Remote Desktop Session Host (1st Server)
- Remote Desktop Session Host (2nd Server)
Follow this related article to plan and install Remote Desktop Services in Windows 2016.
We will use the same server naming convention used in the related article and place the same corresponding roles on the servers.
Install the first Remote Desktop Session Host role on the RDSERVICES server.
Follow the below information to install the Remote Desktop Session Host role on the second server. The second server will be called RDSERVICES2.
Install the Remote Desktop Session Host Server Role on the Second Server
Install a Windows 2016 Server called RDSERVICES2 and join it to the domain.
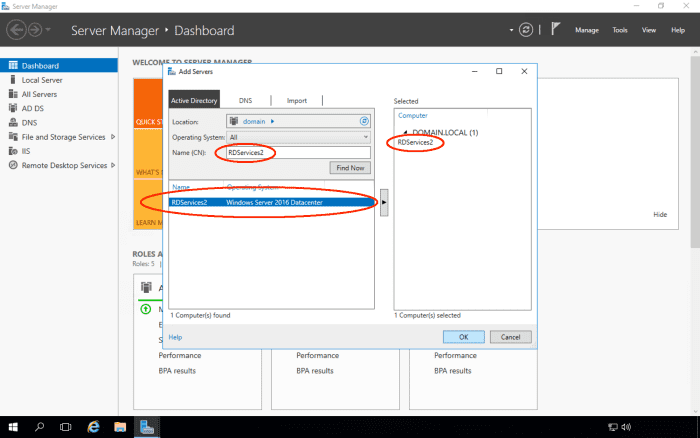
Connect via Remote Desktop to the RDSERVICES server. This was the server we had used to configure Remote Desktop Services from the steps above.
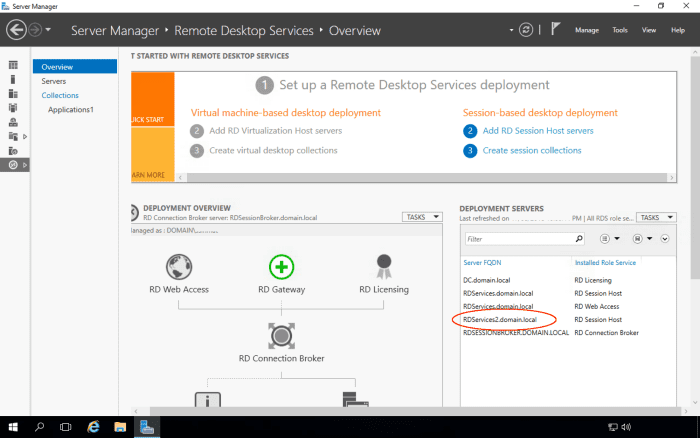
On the RDSERVICES Server, launch Server Manager, and we will add RDSERVICES2 to be managed.
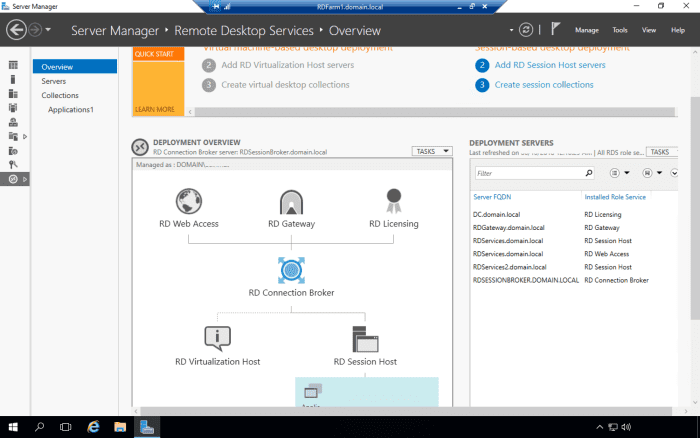
On the left hand pane of Server Manager, click on Remote Desktop Services.
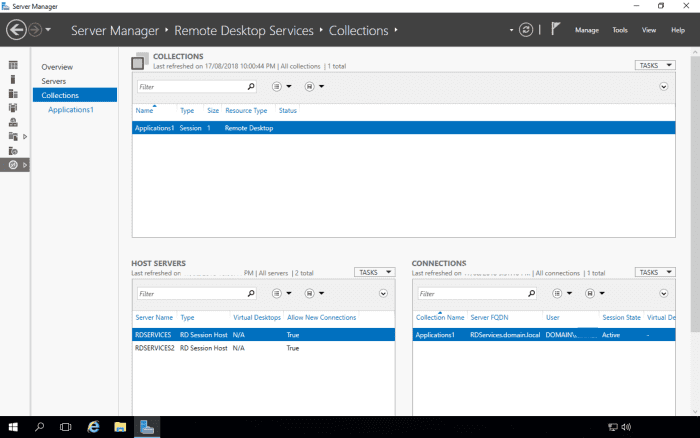
Configure a Collection Across Multiple RD Session Host Servers
We will now configure the Applications1 collection (created in the related article on How to Setup Remote Desktop Services in Windows 2016) also to be hosted on RDSERVICES2.
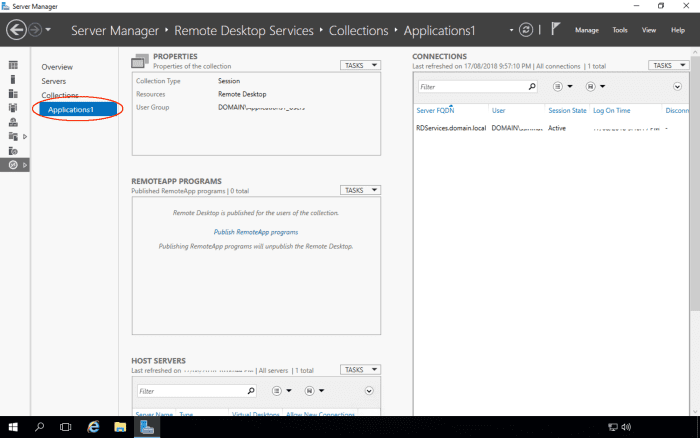
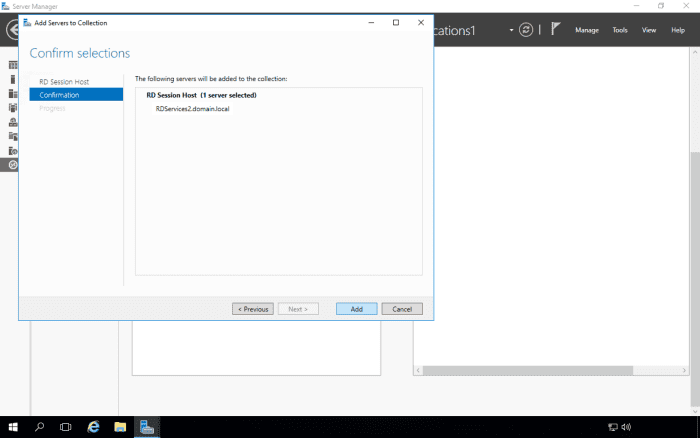
Click on the Applications1 collection.
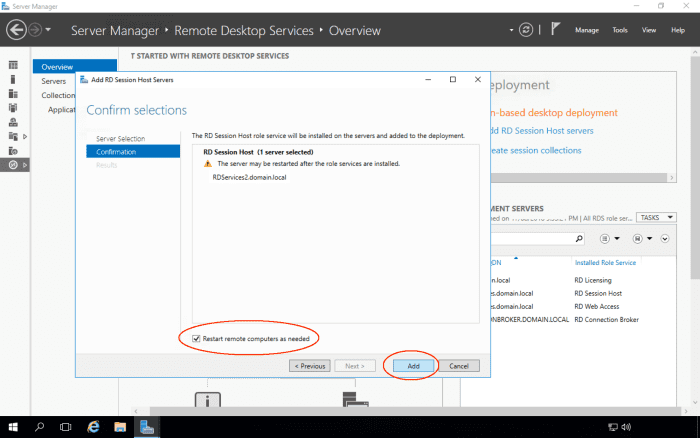
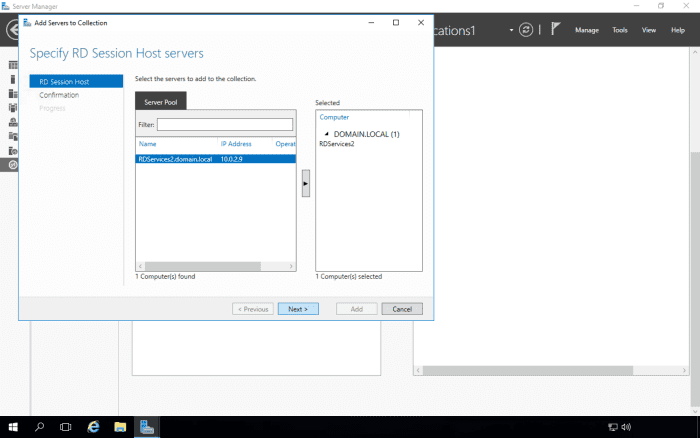
Scroll down to the Host Servers section. Currently, only RDSERVICES is hosting the collection. We will now add RDSERVICE2 to also host the collection.
Select the Add RD Session Host Servers option from the Tasks menu.
Configure Load Balancing
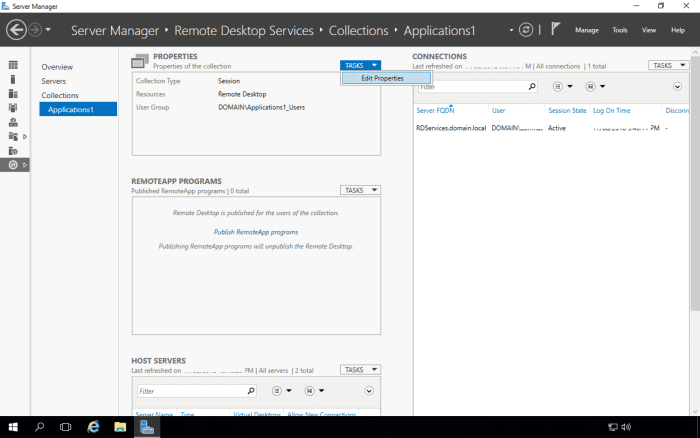
We will now configure the load balancing settings for the Applications1 collection.
Scroll up to the Applications1 properties section.
Select Edit Properties from the Tasks menu.
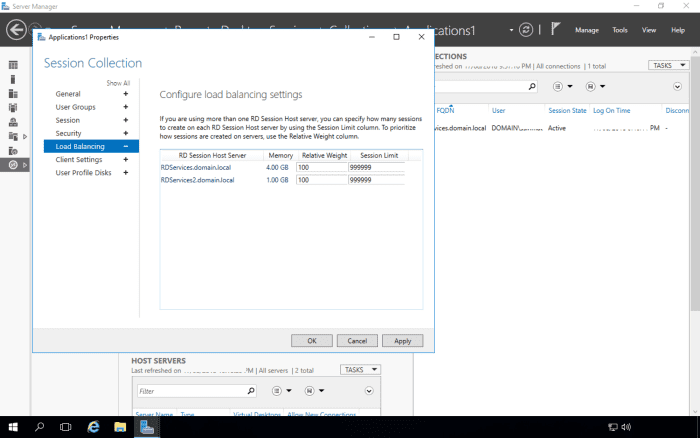
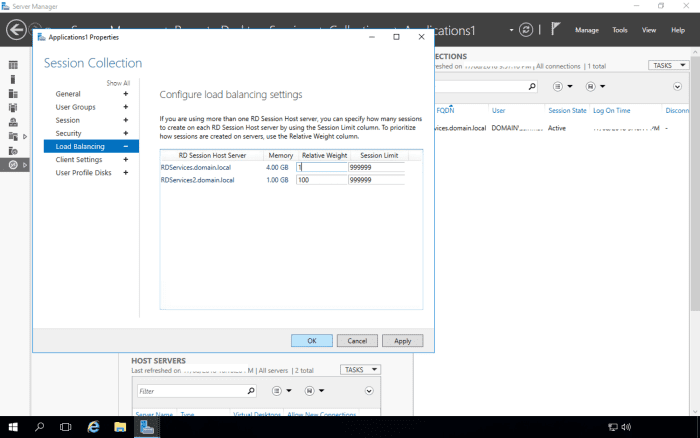
Open up the load balancing section.
The current setting is Relative Weight 100 for both the RD Session Host servers. What this means is both servers will share the user's remote desktop sessions 50-50.
You can increase (or decrease) the relative weight to control which servers will end up having more sessions.
If you want to drain a particular server of users if you are going to be doing maintenance on the server, use a value of 1 for the relative weight of that server, and keep your administrator account logged into that server. This means any new connections will be redirected to the second server. Existing connections will not be affected. As users log off, the server will be drained of user sessions so you can begin doing your maintenance.
Note: You cannot use a value of 0.
Bypassing Connection Broker
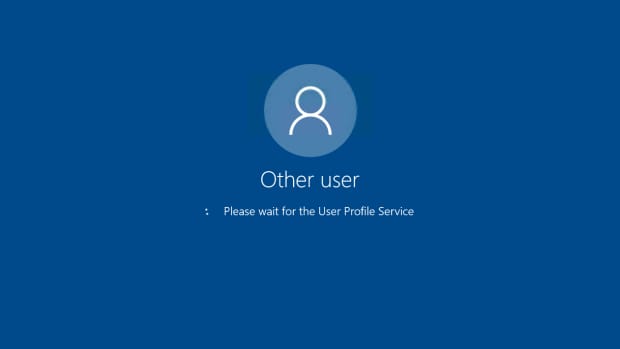
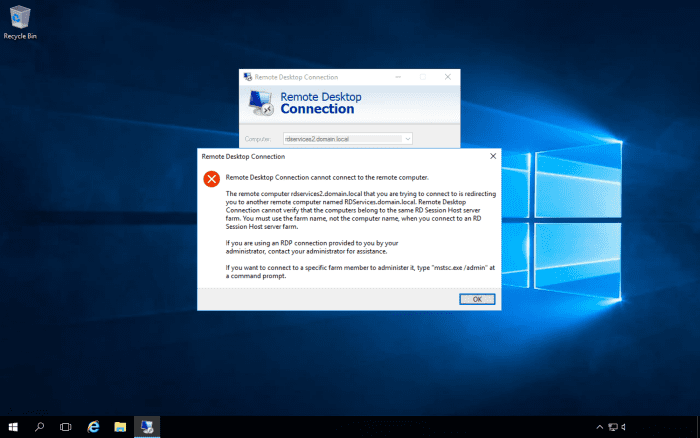
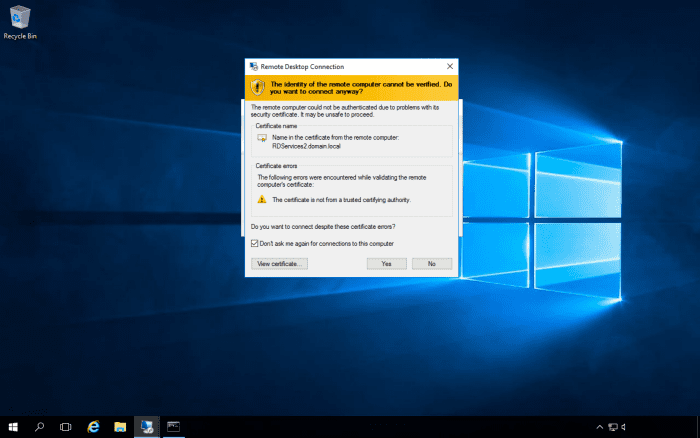
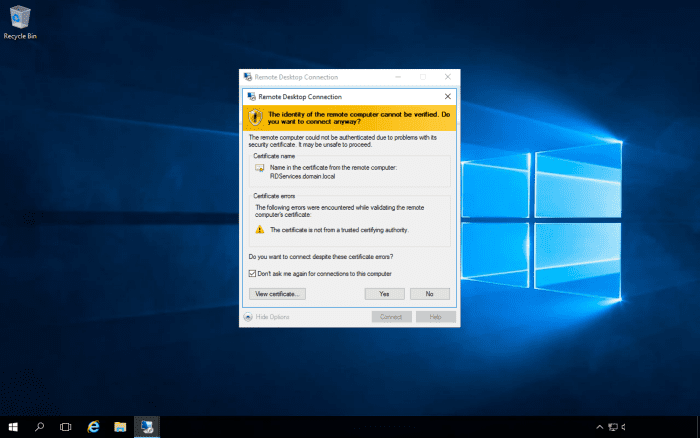
If you try to Remote Desktop to a server that's load balanced and you are using the server's name, you may get an error message. The reason is that the connection broker may try to redirect your session to a different server than the server that you initially tried to connect to. When this happens, you will get the following message:
However, there are times when you really do need to connect to a specific server in the farm. In this case, you will need to start up the Remote Desktop client with the "/a" switch. This can be typed in the command line or the run box.
e.g., mstsc /a
This will launch the Remote Desktop client in administration mode, and its session will not get redirected.
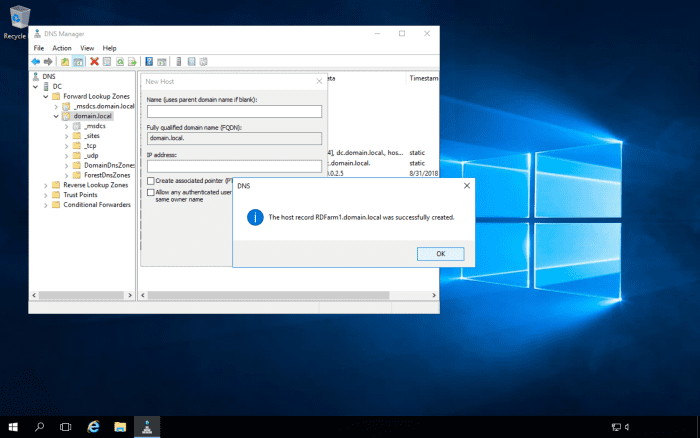
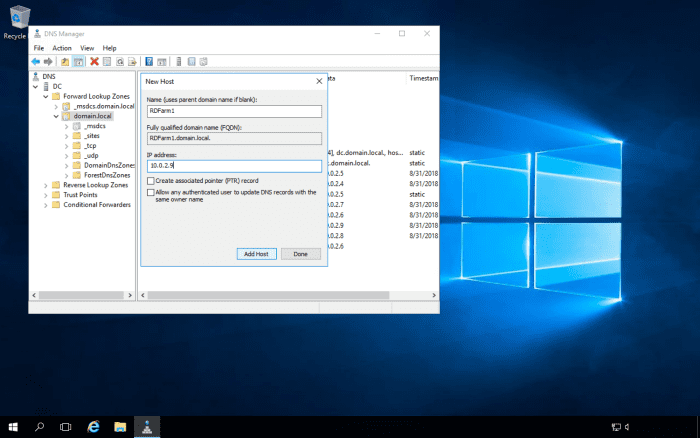
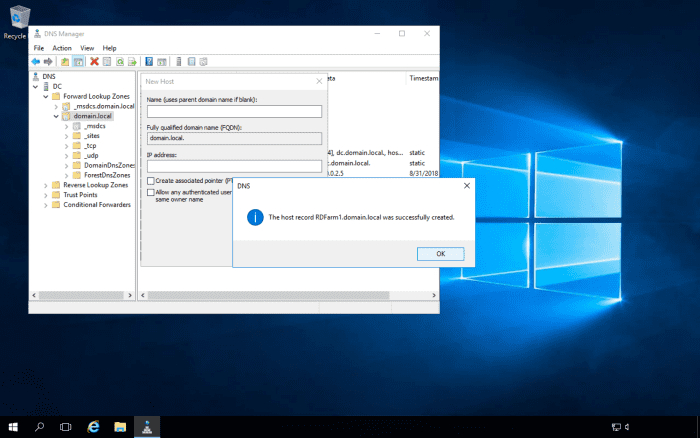
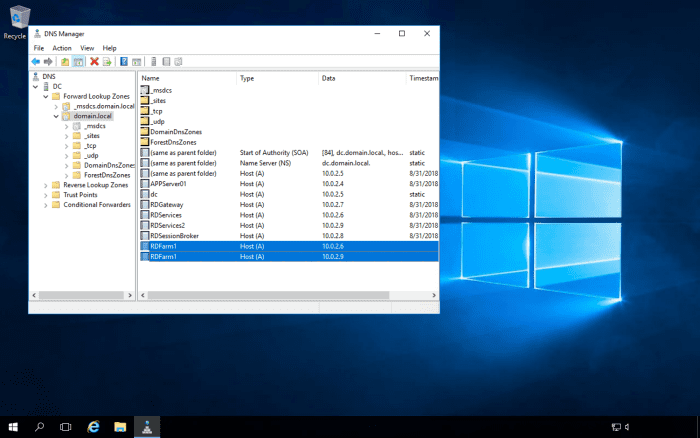
Add DNS Entries for the RD Connection Broker Farm
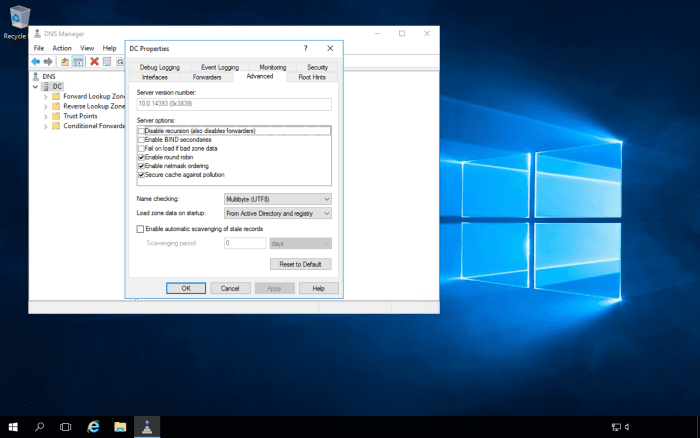
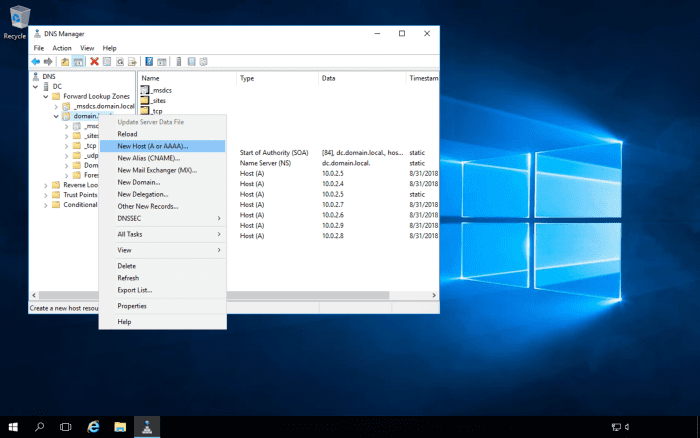
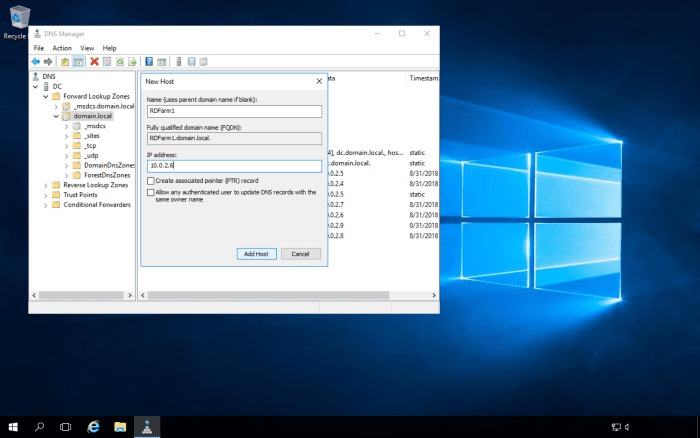
Following on from the above, where you will sometimes get an error message if you try to Remote Desktop into load-balanced servers using one of the server's names, you will need to create DNS entries for the RD Farm. The DNS server should be enabled for round-robin DNS. The RD Farm name can be anything you like, as long as it's accepted by the DNS server e.g., RDFarm. The reason why we need the DNS server to be enabled for round-robin DNS is that we will have multiple entries for the RD Farm name, with each entry pointing to each server's IP address that is in the farm.
Navigate to the DNS zone, and create the DNS entries for the farm.
DNS Round Robin Load-Balancing and Connection Broker
By using the farm DNS name for the server name in the Remote Desktop client, we are using DNS round robin to decide which RD session host server is going to have the initial connection. This is called DNS round-robin load balancing.
Once the user has authenticated to the RD session host server in the farm, the server then contacts the connection broker to determine whether to continue with the login process or to redirect the connection to another RD session host server in the farm.
The connection broker first determines whether the authenticated user account has a disconnected session on one of the servers in the farm. If there is a disconnected session on one of the farm servers, the user will be re-directed to that session. If the user doesn't have a disconnected session in the farm, the broker uses the Session Collection Load Balancing settings to determine which server to redirect to.
An exception to the Session Collection Load Balancing settings, as mentioned previously, is if the remote desktop client was started from the command line or the run box with the "/a" option e.g. mstsc /a.
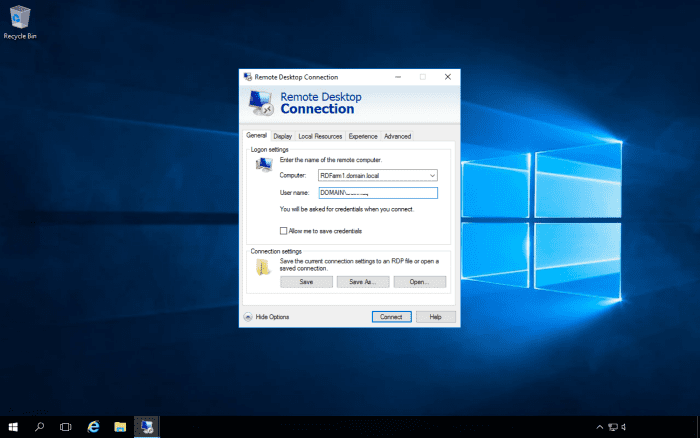
Testing Remote Desktop Connection Broker on the Internal Network
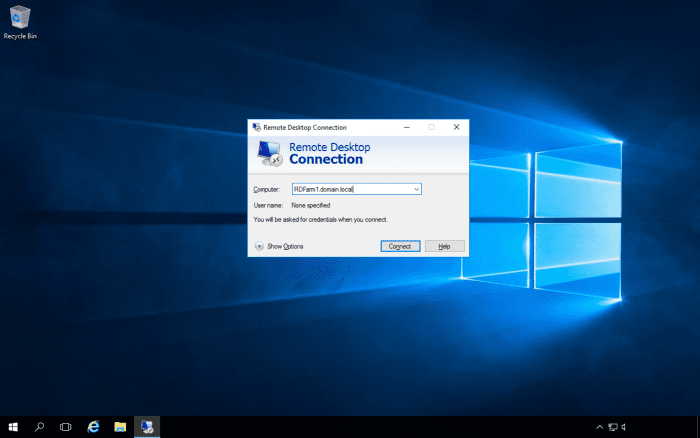
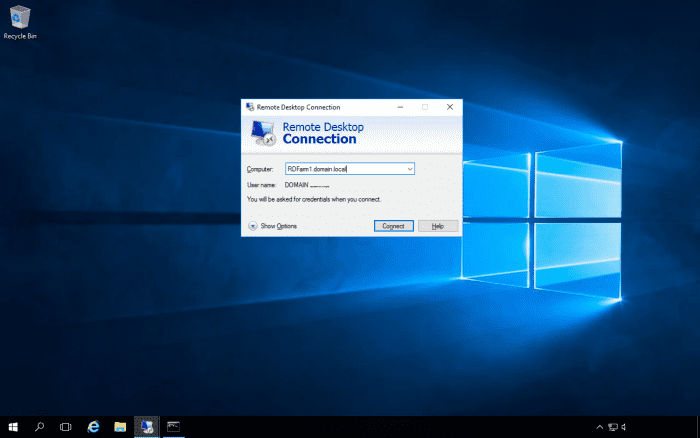
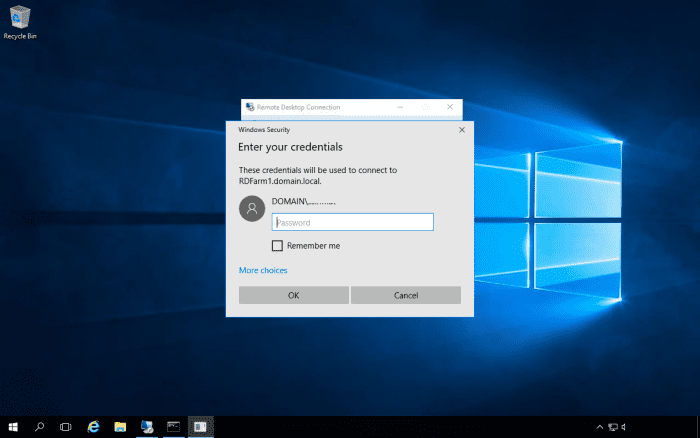
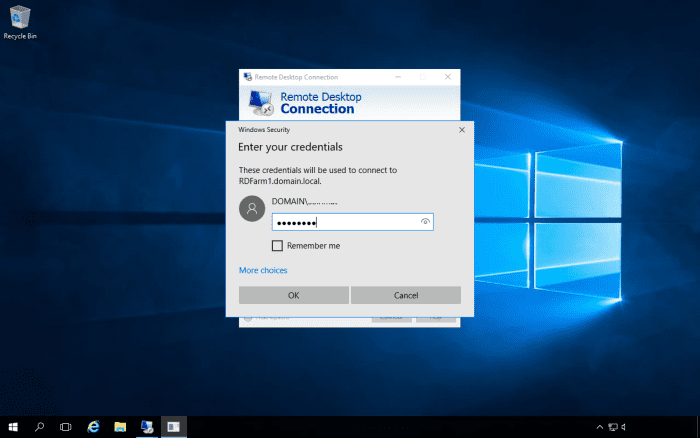
To connect to the farm, use the DNS name of the farm for the computer name in the Remote Desktop client.
To test if the connection broker is doing its job, we can adjust the relative weight of the server that we have just connected to in the farm to 1.
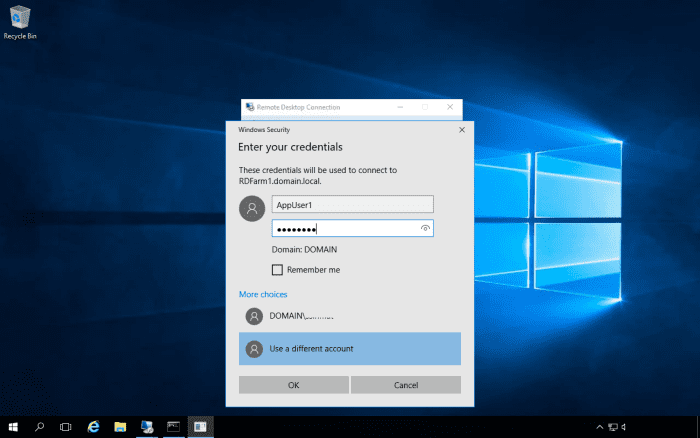
In the above example, we have connected to the RDServices server. We will adjust the relative weight for it to 1. We can then remote desktop into the farm using a second user account and we should see it connect to the second server.
If you have a disconnected user session or even a non-disconnected user session on a server in the farm, the connection broker will redirect your connection to this session if you try to log in as that same account.
To test this, we can remote desktop to the farm as the account that’s currently logged into the RDServices server. Despite the relative weight being 1, the connection broker will redirect the user to the RDServices server.
Summary
We have now completed creating a Remote Desktop Session Host Farm, serving an Application Collection, and managed by the Remote Desktop Connection Broker.
We can connect to the RD Farm on the internal network.
This article is accurate and true to the best of the author’s knowledge. Content is for informational or entertainment purposes only and does not substitute for personal counsel or professional advice in business, financial, legal, or technical matters.






Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar