How to Docker container in GUI Mode?
What is DOCKER?
Docker is an open platform for developing, shipping, and running applications. Docker enables you to separate your applications from your infrastructure so you can deliver software quickly. With Docker, you can manage your infrastructure in the same ways you manage your applications. By taking advantage of Docker’s methodologies for shipping, testing, and deploying code quickly, you can significantly reduce the delay between writing code and running it in production.
Docker is designed to make it easier to create, deploy, and run applications by using containers. Containers allow a developer to package up an application with all of the parts it needs, such as libraries and other dependencies, and deploy it as one package.
The task we want to perform is possible with the Docker file, so let's learn first about the docker file and proceed further...
The Docker platform
Docker provides the ability to package and run an application in a loosely isolated environment called a Container. The isolation and security allow you to run many containers simultaneously on a given host. Containers are lightweight because they don’t need the extra load of a hypervisor, but run directly within the host machine’s kernel. This means you can run more containers on a given hardware combination than if you were using virtual machines. You can even run Docker containers within host machines that are actually virtual machines!
✅ Docker provides tooling and a platform to manage the lifecycle of your containers
- Develop your application and its supporting components using containers.
- The container becomes the unit for distributing and testing your application.
- When you’re ready, deploy your application into your production environment, as a container or an orchestrated service. This works the same whether your production environment is a local data center, a cloud provider, or a hybrid of the two.
What is the Docker file?
A Dockerfile is a text document that contains all the commands a user could call on the command line to assemble an image. Using docker build users can create an automated build that executes several command-line instructions in succession. This page describes the commands you can use in a Dockerfile it is also used for building docker images including the basic requirement of the image like environmental variables, network port, and other components.
There are two types of applications or services that can be used inside a Docker Container, that are:
1. Applications that run as Background Services(like web servers).
2. GUI Applications(like Firefox) that run in Foreground.
Looking to run Firefox or another graphical user interface (GUI) app in Docker containers? Yes!! It is possible.
But using normal docker run commands, you won’t be able to see or interact with the GUI application. You need to connect the display with the container to do so. In this article, we will discuss how to do the same.
“We will see how to run a firefox inside a docker container and interact with it in our host machine”
GUI CONTAINER ON THE DOCKER
Docker is the best tool you can use if you want to develop one single application that can run and work uniformly at any environment, laptop or public cloud instance.
Benefits of Docker
- Test, Roll Back, and Deploy.
- Flexibility.
- Collaboration, Modularity, and Scaling. and many more
After researching about Docker GUI, I concluded that very less used case where the docker container is used for GUI purposes.
You can install Docker Engine in different ways, depending on your needs:
- Most users set up Docker’s repositories and install them for ease of installation and upgrade tasks. This is the recommended approach.
- Some users download the RPM package and install it manually and manage upgrades completely manually. This is useful in situations such as installing Docker on air-gapped systems with no access to the internet.
- In testing and development environments, some users choose to use automated convenience scripts to install Docker.
Install using the repository
Before you install Docker Engine for the first time on a new host machine, you need to set up the Docker repository. Afterward, you can install and update Docker from the repository.
Step:1 Configure Docker Yum Repository
These repositories are included in the docker.repo file above but are disabled by default. You can enable them alongside the stable repository.
[Docker] baseurl = https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/7/x86_64/stable/ gpgcheck = 0 name = Software from docker index repo
Step:2 Installing Docker
To Use Docker Tool we have to Install the Docker Software. To Install Docker Software in RHEL8 Use the command as :
yum install docker-ce --nobest -y
Step 3: Verify the docker installation
we have to check whether the docker software has been installed or not by checking its version
docker --version
Step 4: Start the docker services
For using the docker service, first, we have to start it by using the command “ systemctl start docker “
And then we have to check whether the service has been started or not by using the command “ systemctl status docker “
systemctl start docker systemctl status docker
Step 5: Create a Docker file
we have to create a workspace with any name, in my case, it is Docker_Firefox, and then create a Dockerfile inside the above workspace to create the container with the below configuration.
vim Dockerfile
FROM centos RUN yum install firefox -y RUN yum install PackageKit-gtk3-module libcanberra-gtk2 -y CMD /usr/bin/firefox
Step 6: Build the Docker Image
Now build this image using the docker build command.
docker build -t <image name> .
Here in my case image name is bobby8249/firefox ."bobby8249" is my account name in docker hub. so I use this format so I can push it when I want without change the image name
Docker image created successfully.
We can verify it by the below command.
docker images
Step 7: Launch GUI application On the Docker container
For a GUI Application to run,
Now, run the container using the above-created image
Note:
- docker run -it is used to launch the container
● Share the DISPLAY environment variable to the Container OS
--env="DISPLAY"
● run the OS with the Host’s Network driver
--net=host
These extra arguments are used to set up the base OS environment inside the container
docker run -it --name=GUI_Container --env="DISPLAY" --net=host bobby8249/firefox
Now Firefox is Launch successfully in GUI mode which is running inside the centos container. As you can see the container is running with the same name we have created here our required task is completed ...
Finally, we can run a GUI-based app also in our docker containers, Thanks for learning…….
===========================
Launching GUI App in CentOS Docker Container

Hello Everyone ,
Today I am going to launch GUI Applications like Firefox, Jupyter notebook inside docker container.
Task Description 📄
📌 GUI container on the Docker
🔅 Launch a container on docker in GUI mode
🔅 Run any GUI software on the container
Pre-requisite :
✔ Docker should be installed in a System.
Let’ Start :-
Steps to follow :-
1.Check whether Docker is installed in your system or not, run the following to command to check it out.
docker info
2.To use docker first we have to start docker services. And make it enable so it will be on start mode permanently.
systemctl start docker
systemctl enable docker
3.It’s time to pull image from DockerHub to our base OS Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.
docker pull centos:latest
# Here, I am using CentOS latest image. To see downloaded images in docker
docker images
4.Type “export DISPLAY=:0”
export DISPLAY=:0
What is the meaning of this Command ?
The environment variable DISPLAY tells GUI programs on how to communicate with the GUI. A Unix system can run multiple X servers, i.e. multiple displays. These displays can be physical displays (one or more monitor), or remote displays (forwarded over the network, e.g. over SSH), or virtual displays such as Xvfb, etc. The basic syntax to specify displays is HOST: NUMBER; if you omit the HOST part, the display is a local one.
5.Restart The Docker Service
systemctl restart docker 
# The Service of Docker Should start Otherwise it should give some errors
6.After the start of Docker service then you should type the Docker run command with the use of X11 Port.
docker run -it -v /tmp/.X11-unix/:/tmp/.X11-unix/ -e DISPLAY=$DISPLAY centos bashBefore executing this command, let’s understand what this command will exactly do.
- docker run -ti --rm
-i sets up an interactive session; -t allocates a pseudo tty; --rm makes this container ephemeral.
- -e DISPLAY=$DISPLAY
-e sets the host display to the local machine's display.
- -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix
-v bind mounts the X11 socket residing in /tmp/.X11-unix on your local machine into /tmp/.X11-unix in the container.
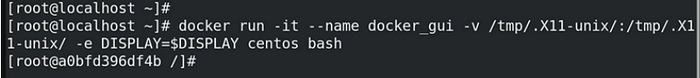
7.Now install any GUI Application inside container. Here I am installing Firefox.
yum install firefox -y
8.Run the “firefox” command, and hopefully, you will see your Firefox Web-Browser is running inside the Docker container.
The Firefox Will take GUI from the Linux port X11.
firefox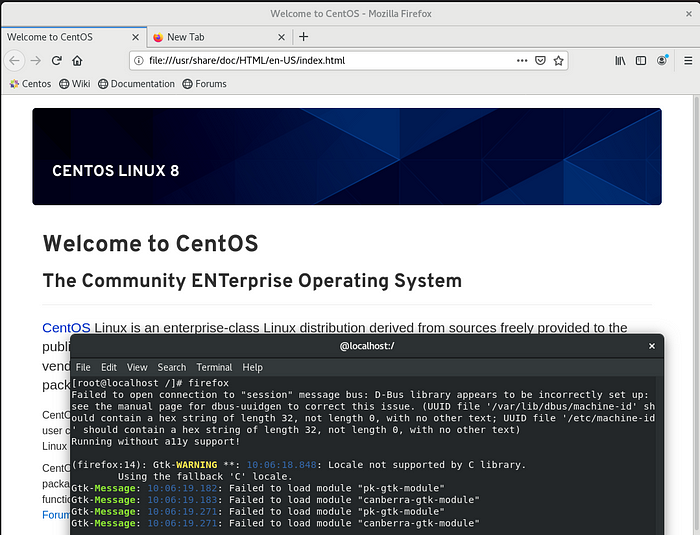
Now it Works perfectly.
We have some warnings but we can also remove that by installing some packages and softwares.
9.Now Let’s install jupyter notebook.
But for installing jupyter notebook we first need to install python3.
yum install python3 -y
pip3 install jupyter
10.Installation is complete launch jupyter notebook.
Note :- We will be launching jupyter notebook in root user so we need to allow root user to use it.
jupyter notebook --allow-root# Now, we got the token, so note this token and give it whenever it requires.
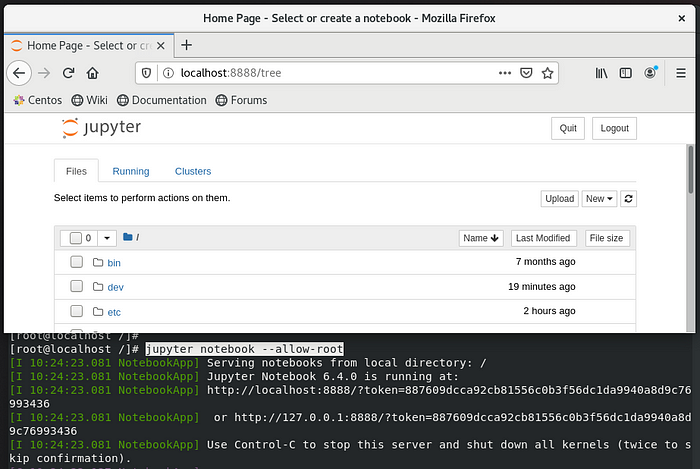
Well Done, we have launched Jupyter Notebook Successfully on Docker Container.
Hope you understood the concept and performed this task with me.
Thank you for reading my article🤗
For any help or suggestions find me on LinkedIn.












Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar