Temperature upload over MQTT using Raspberry Pi and DHT22 sensor
Thingsboard is an open-source server-side platform that allows you to monitor and control IoT devices. It is free for both personal and commercial usage and you can deploy it anywhere. If this is your first experience with the platform we recommend to review what-is-thingsboard page and getting-started guide.
This sample application performs collection of temperature and humidity values produced by DHT22 sensor and further visualization on the real-time web dashboard. Collected data is pushed via MQTT to Thingsboard server for storage and visualization. The purpose of this application is to demonstrate Thingsboard data collection API and visualization capabilities.
The DHT22 sensor is connected to Raspberry Pi. Raspberry Pi offers a complete and self-contained Wi-Fi networking solution. Raspberry Pi push data to Thingsboard server via MQTT protocol by using paho mqtt python library. Data is visualized using built-in customizable dashboard. The application that is running on Raspberry Pi is written on python which is quite simple and easy to understand.
The video below demonstrates the final result of this tutorial.
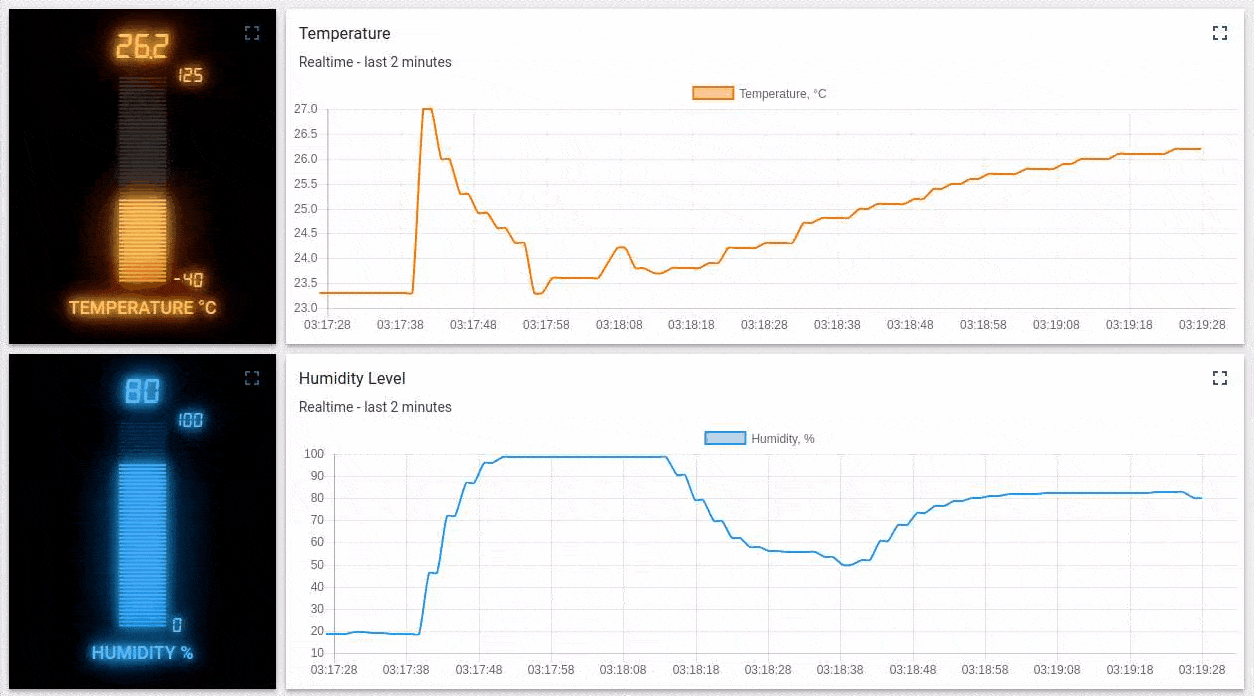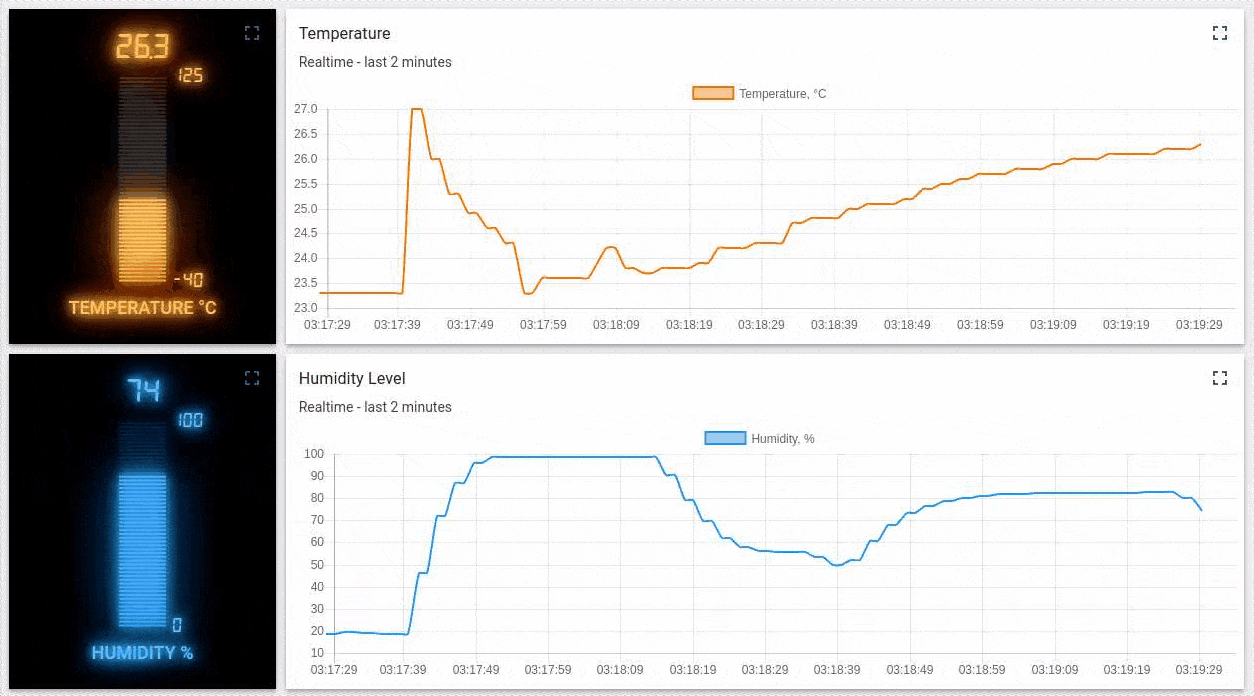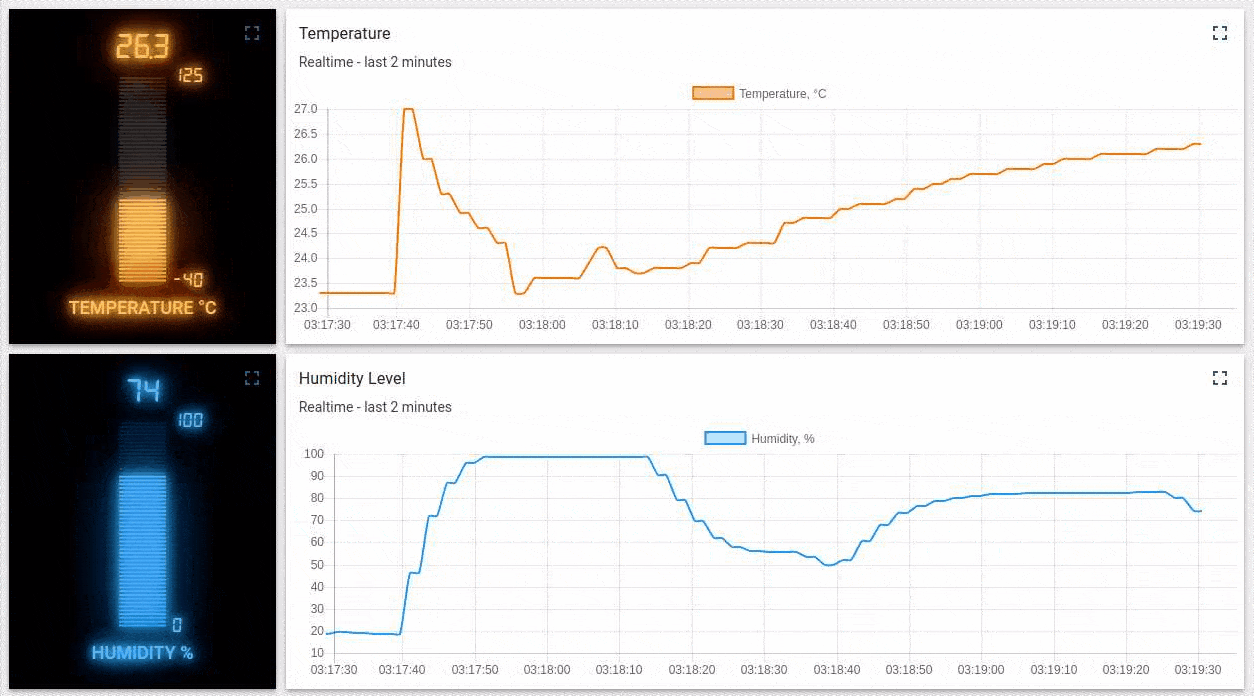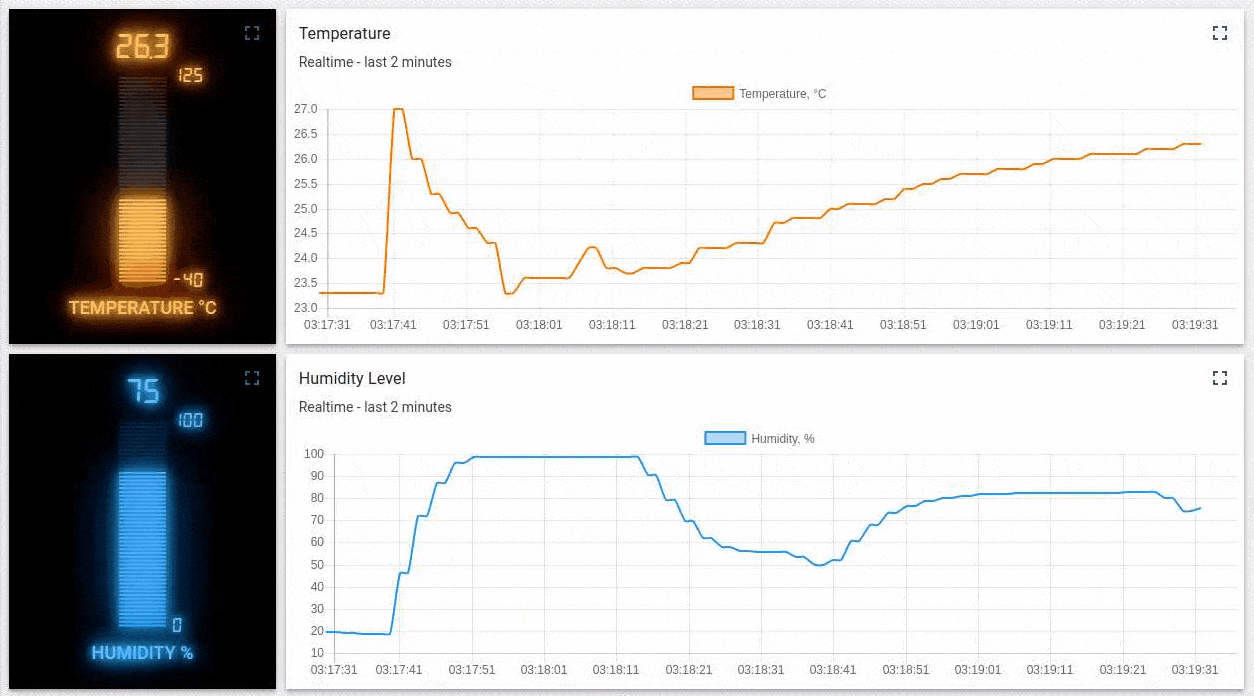
Once you complete this sample/tutorial, you will see your sensor data on the following dashboard.
Prerequisites
You will need to Thingsboard server up and running. Use either Live Demo or Installation Guide to install Thingsboard.
List of hardware and pinouts
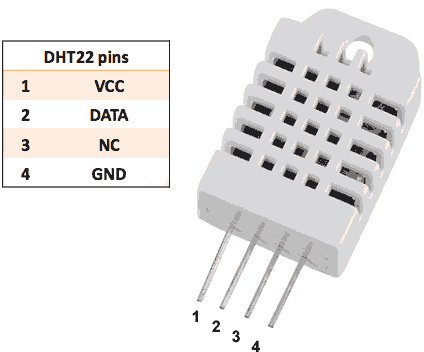
- Resistor (between 4.7K and 10K)
- Breadboard
- 2 female-to-female jumper wires
- 10 female-to-male jumper wires
- 3 male-to-male jumper wire
Wiring schemes
| DHT-22 Pin | Raspberry Pi Pin |
|---|---|
| DHT-22 Data | Raspberry Pi GPIO 4 |
| DHT-22 VCC | Raspberry Pi 3.3V |
| DHT-22 GND (-) | Raspberry Pi GND |
Finally, place a resistor (between 4.7K and 10K) between pin number 1 and 2 of the DHT sensor.
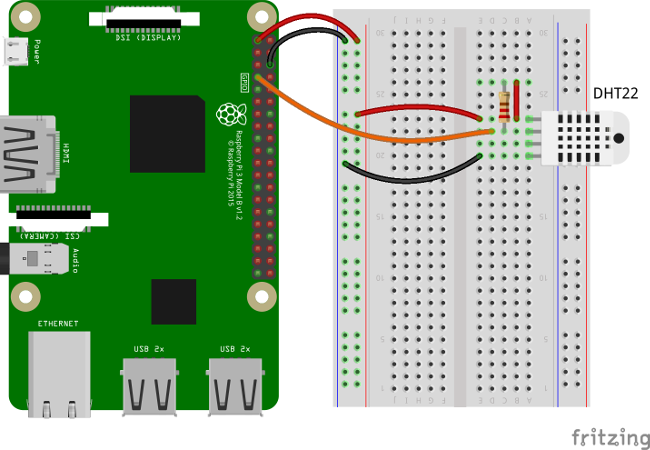
The following picture summarizes the connections for this project:
Thingsboard configuration
Note Thingsboard configuration steps are necessary only in case of local Thingsboard installation. If you are using Live Demo instance all entities are pre-configured for your demo account. However, we recommend to review this steps because you will still need to get device access token to send requests to Thingsboard.
Provision your device
This step contains instructions that are necessary to connect your device to Thingsboard.
Open Thingsboard Web UI (http://localhost:8080) in browser and login as tenant administrator
- login: tenant@thingsboard.org
- password: tenant
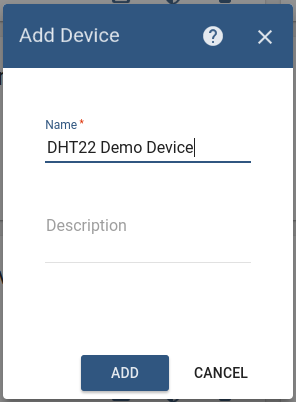
Goto “Devices” section. Click “+” button and create device with name “DHT22 Demo Device”.
Once device created, open its details and click “Manage credentials”. Copy auto-generated access token from the “Access token” field. Please save this device token. It will be referred to later as $ACCESS_TOKEN.
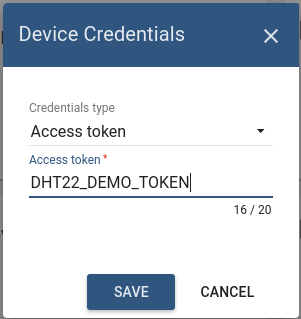
Click “Copy Device ID” in device details to copy your device id to clipboard. Paste your device id to some place, this value will be used in further steps.
Provision your dashboard
This step contains instructions that are necessary to provision new dashboard with map widgets to Thingsboard.
Open “Terminal” and download file containing demo dashboard JSON:
curl -L https://thingsboard.io/docs/samples/raspberry/resources/dht22_temp_dashboard.json > dht22_temp_dashboard.json
Update dashboard configuration with your device Id (obtained in previous step) by issuing the following command:
sed -i "s/{DEVICE_ID}/<your device id>/" dht22_temp_dashboard.json
Obtain JWT token by issuing login POST command:
curl -X POST --header 'Content-Type: application/json' --header 'Accept: application/json' -d '{"username":"tenant@thingsboard.org", "password":"tenant"}' 'http://localhost:8080/api/auth/login'
You will receive response in the following format:
{"token":"$YOUR_JSON_TOKEN", "refreshToken": "$REFRESH_TOKEN"}
copy $YOUR_JSON_TOKEN to some place. Note that it will be valid for 15 minutes by default.
Execute dashboard upload command:
curl -X POST --header 'Content-Type: application/json' --header 'Accept: application/json' --header 'X-Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_JSON_TOKEN' -d "@dht22_temp_dashboard.json"'http://localhost:8080/api/dashboard'
Programming the Raspberry Pi
MQTT library installation
Following command will install MQTT Python library:
sudo pip install paho-mqtt
Adafruit DHT library installation
Install python-dev package:
sudo apt-get install python-dev
Downloading and install the Adafruit DHT library:
git clone https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit_Python_DHT.git
cd Adafruit_Python_DHT
sudo python setup.py install
Application source code
Our application consists of single python script that is well commented. You will need to modify THINGSBOARD_HOST constant to match your Thingsboard server installation IP address or hostname. Use “demo.thingsboard.io” if you are using live demo server.
The value of ACCESS_TOKEN constant corresponds to sample DHT22 demo device. If you are using live demo server - get the access token for pre-provisioned “DHT22 Demo Device”.
Running the application
This simple command will launch the application:
python mqtt-dht22.py
Data visualization
Finally, open Thingsboard Web UI. You can access this dashboard by logging in as a tenant administrator.
In case of local installation:
- login: tenant@thingsboard.org
- password: tenant
In case of live-demo server:
- login: your live-demo username (email)
- password: your live-demo password
See live-demo page for more details how to get your account.
Go to “Devices” section and locate “DHT22 Demo Device”, open device details and switch to “Latest telemetry” tab. If all is configured correctly you should be able to see latest values of “temperature” and “humidity” in the table.
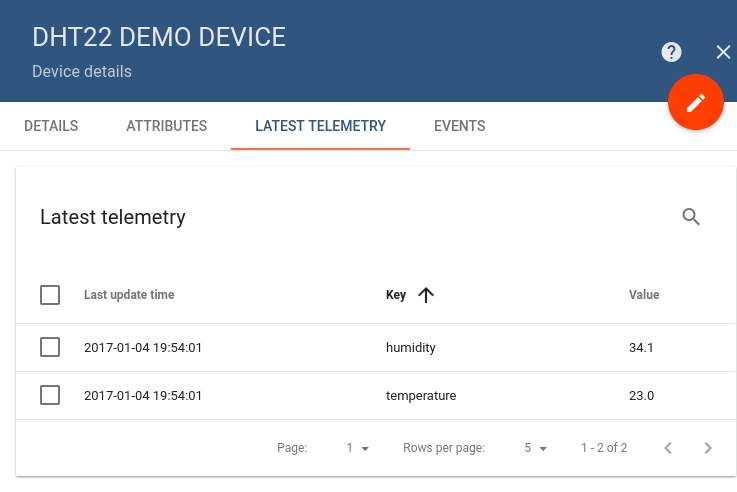
After, open “Dashboards” section then locate and open “DHT22: Temperature & Humidity Demo Dashboard”. As a result you will see two digital gauges and two time-series charts displaying temperature and humidity level (similar to dashboard image in the introduction).
Next steps
Browse other samples or explore guides related to main Thingsboard features:
- Device attributes - how to use device attributes.
- Telemetry data collection - how to collect telemetry data.
- Using RPC capabilities - how to send commands to/from devices.
- Rule Engine - how to use rule engine to analyze data from devices.
- Data Visualization - how to visualize collected data.

Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar