How do I create a high-availability configuration with Synology NAS?
Details
With Synology High Availability (SHA) you may deploy a high-availability solution to ensure uninterrupted services. SHA allows you to combine two Synology NAS devices into a high-availability cluster, ensuring non-stop storage services with maximized system availability.
This tutorial guides you through the process of creating a high-availability solution with your Synology NAS. If you can't find what you need here, please refer to this white paper for more information.
Contents
Resolution
What is Synology High Availability?
The term "high-availability" refers to a server layout solution designed to reduce service interruptions caused by server malfunctions. Synology High Availability (SHA) employs two hosts to form a "high-availability cluster" in which one host assumes the role of "active server" and the other host acts as a standby "passive server."
In a high-availability cluster, data on the active server is continuously replicated to the passive server, so mirrored copies of all files will exist on both hosts. Therefore, in the event the active server crashes or malfunctions, the passive server can take over all services, minimizing system downtime.
Before you start
Please read the following sections carefully before trying to create a high-availability cluster.
Hardware Requirements:
- SHA requires two identical Synology NAS to act as active and passive servers.
- Two different Synology NAS can act as active and passive servers, but with limitations. For more details, please see this article.
System Requirements:
- The active and passive servers must be identical models and both support Synology High Availability.
- The same version of DSM and package must be installed on both hosts.
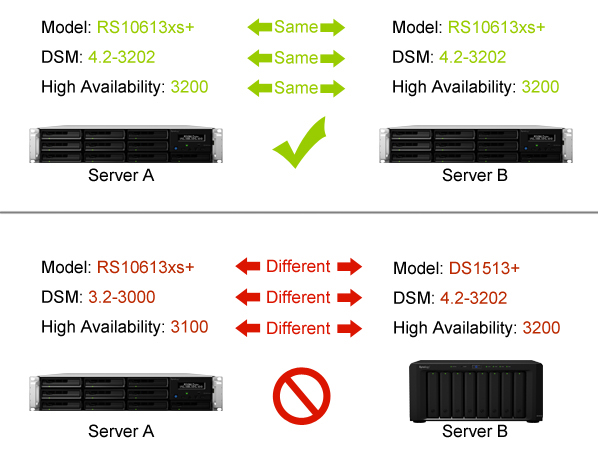
The illustration above is for reference only. Your model and DSM version may differ.
Volume and Disk:
- The drive capacity of both hosts must be identical to avoid data inconsistencies.
- The active and passive servers must have the same number of drives. In addition, drive position must be identical.
- The hosts cannot contain any SHR format volumes. Go to Storage Manager > Volume to make sure no SHR volumes exist.
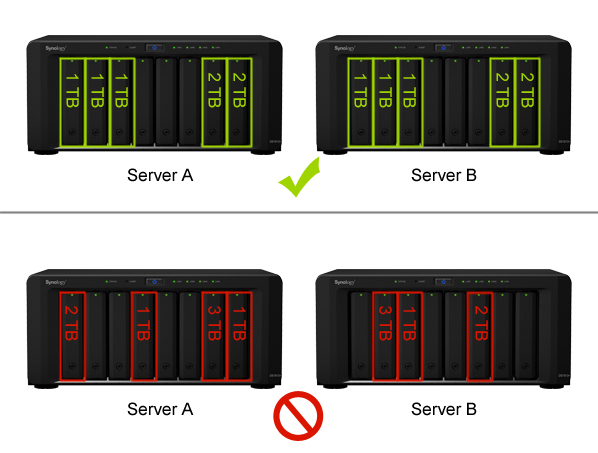
The illustration above is for reference only. The number and size of disks in your environment may differ.
Network Environment:
- Both hosts must be assigned static IP addresses as the cluster connection. Make sure that the IP addresses of both hosts are accessible and belong to the same subnet; otherwise, errors might occur when performing a switchover to the passive server. To change network settings, log in to each host and go to Control Panel > Network > Network Interface, select the network interface and click Edit.
- Both hosts must have the same number of LAN ports. If the hosts are equipped with additional network interface cards, these network cards will also count as additional LAN ports.
- Synology High Availability does not support the following: DHCP, DHCP server, IPv6, PPPoE, and Wi-Fi. Please ensure that the above are all switched off before creating a high-availability cluster.
Cable the hosts
In this section, we'll explain how to connect both hosts so that a high-availability cluster can be created. Please see the following steps:
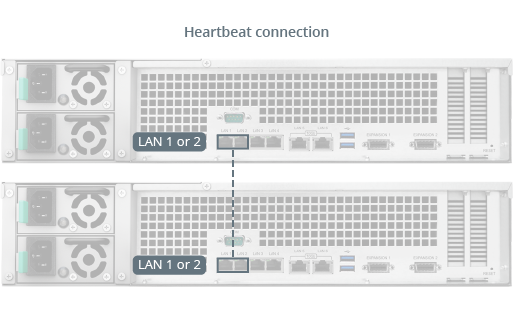
- Use a network cable to connect the two hosts to each other. This connection shall serve as the Heartbeat connection between the two hosts, facilitating communication and allowing data to be replicated from the active server to the passive server. This connection must meet the following criteria:
- Use the same network interface on both hosts. For example, if one end is connected to LAN 1 on one host, then the other end must be connected to LAN 1 on the other host.
- Use the fastest network interface on both hosts. If the hosts are equipped with 10GbE add-on network interface cards, this connection must use them.
- Connect the two hosts directly, without passing through any switches or routers.
- Use network cables to connect the two hosts to the network using the remaining network interfaces. Make sure these connections are active and belong to the same network. In order to prevent service interruptions caused by network failure, we recommend deploying multiple switches in your network environment so that each host in the high-availability cluster can be connected to a separate switch.
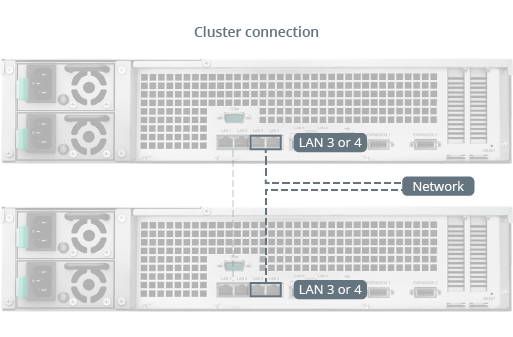
- The hosts are now ready to create a high-availability cluster. Please continue with the steps below.
Create a high-availability cluster with the hosts
Once the two hosts are connected properly, you can follow the steps below to create a high-availability cluster.
- Log into the host that you want to assume the role of the active server with an account belonging to the administrators group.
- Open Synology High Availability.
- Click Create high-availability cluster to start the cluster creation wizard.
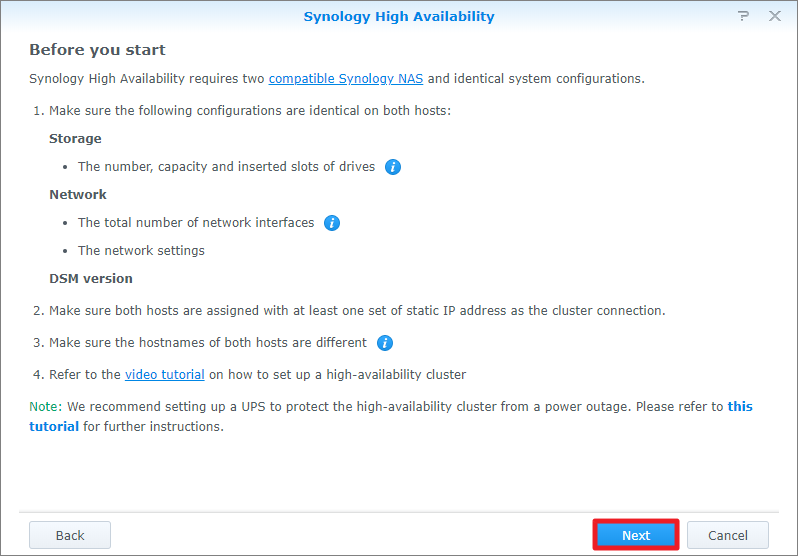
- Click Next.
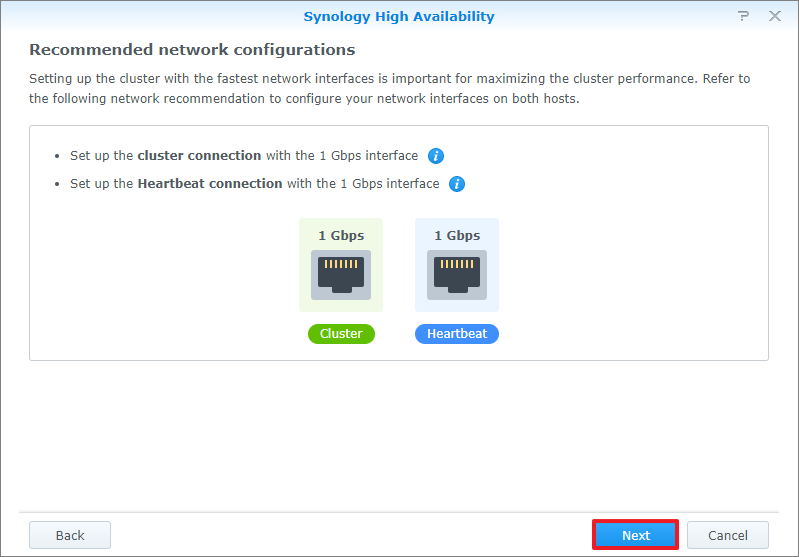
- Select which network interfaces to use for the high-availability cluster's cluster connection and Heartbeat connection. Then click Next.
- Enter the credentials of an account belonging to the administrators group on the passive server. Then click Next.
- Specify a name for the high-availability cluster and the IP address with which you'll be able to access the cluster resources. The wizard will display the available IP range; please select an IP address that has not been used by other services in the network. Then click Next.
- The wizard will check if the system meets all the requirements. Click Next when the verification is done.
- If there are existing data, volume or LUN detected on the active server, you can choose to keep the data or erase it all. Click Next to continue.
- Confirm the settings you previously made. Then click Apply.
- Tick the checkbox after reading the instructions and then click Yes.
- The wizard will start to create the high-availability cluster. Creation time varies depending on your environment.
- Once finished, you'll see the cluster status on the Cluster page.
Resolve errors after auto failover occurs
When certain errors occur, the system can automatically failover services from the active server to the passive server. This event is called an "auto failover." The system might initiate failover in the situations below.
Crashed storage space:
Auto failover will occur when a storage space (e.g. volume, iSCSI LUN) on the active server has crashed, but the corresponding storage space on the passive server is functioning normally.1 For example, if Host A is the active server and Host B is the passive server, the system will perform an auto failover when a storage space crashes on Host A, and the corresponding storage space is healthy on Host B.
After the auto failover process has finished, please do the following:
- Go to the Storage page and identify the disks which are missing or crashed on Host A (which is now the passive server).
- If there are missing disks, please install disks in the corresponding slots so both hosts have the same amount of disks.
- If there are crashed disks, please replace them.
- Confirm that both hosts contain identical disk configurations, and the status of all the disks are Normal or Not Initialized.
- Go to the Storage page and click Repair to fix the storage space.
Service error:
Auto failover will occur when an error occurs on a monitored service. For example, if a monitored service on Host A (the active server) malfunctions, the system will automatically failover to Host B. In this case, please do the following once the auto failover is complete.
- Go to the Host page.
- Host A should now be the passive server, so click the Power button > Shutdown.
- Once Host A has completely shut down, power it on again.
Power failure:
Auto failover will occur when the active server is shut down, rebooted, both power units fail, or external power is lost. For example, if Host A is the active server and its power supply fails, the system will failover to Host B. Once power has been restored, please power on Host A (which is now the passive server).
Maintain the high-availability cluster
For routine maintenance procedures, please see the following instructions.
Procedure | Instructions |
|---|---|
Change active server to passive server |
|
Remove passive server from cluster |
|
Add a new passive server |
|
Remove the high-availability cluster and return the hosts to standalone status |
|
Update system/package |
|
Notes:
- The system will not initiate an auto failover if no volume or iSCSI LUN (Block-Level) exists on the crashed storage space.
- SSH and NTP server will be automatically enabled on the active server once the high-availability cluster is created.
- For more information on the applied Synology NAS models of Synology High Availability, please refer to here.
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar