How to Install and Use Checkmk Monitoring Server on Ubuntu 20.04
Checkmk is a monitoring software written in Python and C++. This self-contained tool combines with Nagios and its add-ons and can be used for monitoring your infrastructure and services. Checkmk works in client-server architecture, meaning you must install Checkmk agent on each computer that you want to monitor. With Checkmk, you can monitor web servers, database servers, and cloud infrastructure such as, Azure, AWS and more.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install and use the Checkmk monitoring server on Ubuntu 20.04.
Prerequisites
- A fresh Ubuntu 20.04 server on the Atlantic.Net Cloud Platform
- A root password configured on your server
Step 1 – Create Atlantic.Net Cloud Server
First, log in to your Atlantic.Net Cloud Server. Create a new server, choosing Ubuntu 20.04 as the operating system, with at least 2GB RAM. Connect to your Cloud Server via SSH and log in using the credentials highlighted at the top of the page.
Once you are logged in to your Ubuntu 20.04 server, run the following command to update your base system with the latest available packages.
apt-get update -y
Step 2 – Install Checkmk
By default, Checkmk is not included in the Ubuntu default repository, so you will need to download Checkmk package from its official website:
First, download the Checkmk with the following command:
wget https://download.checkmk.com/checkmk/1.6.0p20/check-mk-raw- 1.6.0p20_0.focal_amd64.deb
Once the download is completed, install the downloaded package with the following command:
dpkg -i check-mk-raw-1.6.0p20_0.focal_amd64.deb
Next, run the following command to install the required dependencies for Checkmk.
apt-get install -f
Once the installation has been completed, run the following command to list all commands available with Checkmk:
omd
You should get the following output:
Usage (called as root): omd help Show general help omd setversion VERSION Sets the default version of OMD which will be used by new sites omd version [SITE] Show version of OMD omd versions List installed OMD versions omd sites Show list of sites omd create SITE Create a new site (-u UID, -g GID) omd init SITE Populate site directory with default files and enable the site omd rm SITE Remove a site (and its data) omd disable SITE Disable a site (stop it, unmount tmpfs, remove Apache hook) omd enable SITE Enable a site (reenable a formerly disabled site) omd mv SITE NEWNAME Rename a site omd cp SITE NEWNAME Make a copy of a site omd update SITE Update site to other version of OMD omd start [SITE] [SERVICE] Start services of one or all sites omd stop [SITE] [SERVICE] Stop services of site(s) omd restart [SITE] [SERVICE] Restart services of site(s) omd reload [SITE] [SERVICE] Reload services of site(s) omd status [SITE] [SERVICE] Show status of services of site(s) omd config SITE ... Show and set site configuration parameters omd diff SITE ([RELBASE]) Shows differences compared to the original version files omd su SITE Run a shell as a site-user omd umount [SITE] Umount ramdisk volumes of site(s) omd backup SITE [SITE] [-|ARCHIVE_PATH] Create a backup tarball of a site, writing it to a file or stdout omd restore [SITE] [-|ARCHIVE_PATH] Restores the backup of a site to an existing site or creates a new site omd cleanup Uninstall all Check_MK versions that are not used by any site. General Options: -V <version> set specific version, useful in combination with update/create omd COMMAND -h, --help show available options of COMMAND
Step 3 – Create a Monitoring Instance
Next, you will need to create a monitoring instance for testing purposes. You can create it using the omd tool:
omd create myserver
You will should see the following output:
Adding /opt/omd/sites/myserver/tmp to /etc/fstab. Creating temporary filesystem /omd/sites/myserver/tmp...OK Restarting Apache...OK Created new site myserver with version 1.6.0p20.cre. The site can be started with omd start myserver. The default web UI is available at http://ubuntu2004/myserver/ The admin user for the web applications is cmkadmin with password: RCDM5jQG (It can be changed with 'htpasswd -m ~/etc/htpasswd cmkadmin' as site user. ) Please do a su - myserver for administration of this site.
Note: Please remember the checkmk username and password from the above output. You will need it to access the Checkmk dashboard.
Next, start the server with the following command:
omd start myserver
You should get the following output:
Starting mkeventd...OK Starting rrdcached...OK Starting npcd...OK Starting nagios...OK Starting apache...OK Initializing Crontab...OK
You can verify the status of the server with the following command:
omd status
You should get the following output:
Doing 'status' on site myserver: mkeventd: running rrdcached: running npcd: running nagios: running apache: running crontab: running ----------------------- Overall state: running
To check the omd version, run the following command:
omd version
Output:
OMD - Open Monitoring Distribution Version 1.6.0p20.cre
You can also see your all monitoring instances with the following command:
omd sites
Output:
SITE VERSION COMMENTS myserver 1.6.0p20.cre default version
Step 4 – Access Checkmk Web Interface
Now, open your web browser and access the Checkmk web interface using the URL http://your-server-ip/myserver. You will be redirected to the Checkmk login page:
Provide your Checkmk username, password and click on the Login button. You should see the Checkmk dashboard in the following screen:
It is a good idea to change the default Checkmk password. Click on the WATO – Configuration in the left side and you should see the following screen:
Set your new password and click on the Save button to change the password.
Step 4 – Create a Monitoring Host
Before starting, you will need to download and install the Checkmk monitoring agent on the server.
In the WATO – Configuration menu, click on the Monitoring Agents, you should see agent packages for all operating systems in the following page:
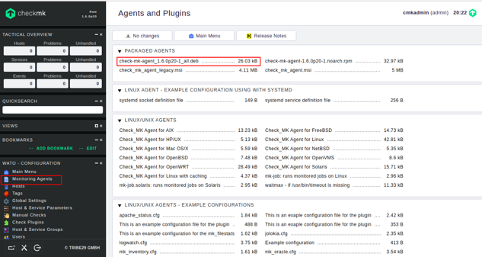
Pick the package for Ubuntu and download it with the following command:
wget http://45.58.38.223/myserver/check_mk/agents/check-mk-agent_1.6.0p20-1_all.deb
Once downloaded, install the agent package with the following command:
dpkg -i check-mk-agent_1.6.0p20-1_all.deb
Once the agent package is installed, you can verify it with the following command:
check_mk_agent | less
You should get the following output:
<<<check_mk>>> Version: 1.6.0p20 AgentOS: linux Hostname: ubuntu2004 AgentDirectory: /etc/check_mk DataDirectory: /var/lib/check_mk_agent SpoolDirectory: /var/lib/check_mk_agent/spool PluginsDirectory: /usr/lib/check_mk_agent/plugins LocalDirectory: /usr/lib/check_mk_agent/local <<<df>>>
In the WATO – Configuration menu, click on the Hosts button. You should see the following page:
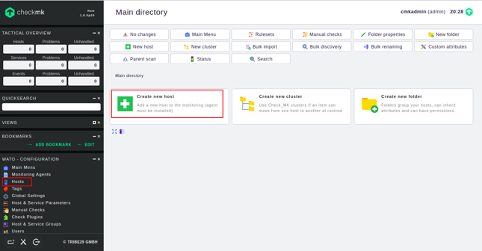
Click on the Create new host button. You should see the following page:
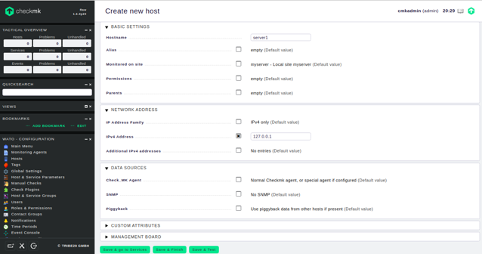
Provide all required information and click on the Save and go to Services button. You should see all services in the following page:
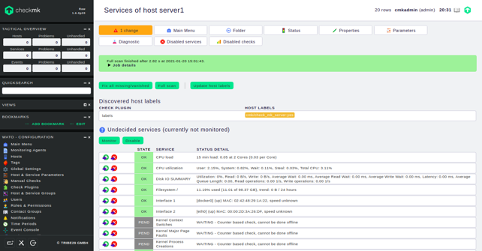
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have successfully installed and configured a Checkmk monitoring server on Ubuntu 20.04. You can now install Checkmk agents on the remote machines and start monitoring from the Checkmk web interface. Try it today using a dedicated server from Atlantic.Net!
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar