Multiple Node OpenStack ‘Liberty’ Installation on CentOS 7.x
by Pradeep Kumar · Published · Updated
OpenStack is an open source cloud software which provides infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS). It can be installed on single and multiple nodes.
In this article we will deploy openStack on three nodes ( compute + controller + network ) on CentOS 7.x using RDO repository and packstack utility. For Single Node OpenStack Installation refer the below :
In article i am using three virtual machines hosted on VirtualBox and each VM has a single LAN interface. Below are architecture details :
Controller Node Details :
- Hostname = controller.example.com
- IP Address = 192.168.1.30
- OS = CentOS 7.x
- DNS = 192.168.1.11
Following OpenStack Components will installed on controller node :
- Keystone
- Glance
- swift
- Cinder
- Horizon
- Neutron
- Nova novncproxy
- Novnc
- Nova api
- Nova Scheduler
- Nova-conductor
Compute Node Details :
- Hostname = compute.example.com
- IP Address = 192.168.1.31
- OS = CentOS 7.X
- DNS = 192.168.1.11
Following OpenStack Components will installed on compute node :
- Nova Compute
- Neutron – Openvswitch Agent
Network Node Details :
- Hostname = network.example.com
- IP Address = 192.168.1.32
- OS = CentOS 7.x
- DNS = 192.168.1.11
Following OpenStack Components will installed on network node :
- Neutron Server
- Neturon DHCP agent
- Neutron- Openswitch agent
- Neutron L3 agent
Perform the Following Steps for Installation :
Step:1 Update the nodes using below command.
Use the below command on all three nodes to update all installed packages.
# yum -y update ; reboot
Step:2 Update /etc/hosts file and Hostname
Set the hostname on all the three nodes using below command , in case it is not set.
# hostnamectl set-hostname 'new_hostname'
Update the /etc/hosts file if you don’t have your local DNS configured.
192.168.1.30 controller.example.com controller 192.168.1.31 compute.example.com compute 192.168.1.32 network.example.com network
Step:3 Disable SELinux and Network Manager on all three nodes.
Use below command to disable SELinux on all three nodes.
# setenforce 0
Disabled SELinux permanently by the changing the parameter ‘SELINUX=disabled’ in the file ‘/etc/sysconfig/selinux‘
Use below commands to disable Network Manager on all three nodes.
# systemctl stop NetworkManager # systemctl disable NetworkManager # reboot
Step:4 Set Passwordless authentication from Controller node to Compute & Network Node.
Run the below commands from Controller node.
[root@controller ~]# ssh-keygen [root@controller ~]# ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@192.168.1.31 [root@controller ~]# ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@192.168.1.32
Now check :
[root@controller ~]# ssh compute Last login: Sun Apr 3 00:03:44 2016 from controller.example.com [root@compute ~]# hostname compute.example.com [root@compute ~]# [root@controller ~]# ssh network Last login: Sun Apr 3 00:04:20 2016 from controller.example.com [root@network ~]# hostname network.example.com [root@network ~]#
Step:5 Enable RDO repository and install packstack utility
Use below yum command to enable RDO repository and install packstack utility only on controller node.
[root@controller ~]# yum install -y https://www.rdoproject.org/repos/rdo-release.rpm [root@controller ~]# yum install -y openstack-packstack
Step:6 Generate and customize answer file
Use below command to generate answer file.
[root@controller ~]# packstack --gen-answer-file=/root/answer.txt [root@controller ~]#
Edit the answer file and Specify the ip address of controller, compute and network node. Apart from this also specify the passwords of different services and disable the components like Demo version and Ceilometer.
[root@controller ~]# vi /root/answer.txt ........................................ CONFIG_CONTROLLER_HOST=192.168.1.30 CONFIG_COMPUTE_HOSTS=192.168.1.31 CONFIG_NETWORK_HOSTS=192.168.1.32 CONFIG_PROVISION_DEMO=n CONFIG_CEILOMETER_INSTALL=n CONFIG_HORIZON_SSL=y CONFIG_NTP_SERVERS=<Specify NTP Server IP > CONFIG_KEYSTONE_ADMIN_PW=<Specify New_Password> ..........................................
Note : In case if you have don’t NTP server then you can leave NTP parameter as it is, but it is highly recommended that we should use ntp server for time syncing.
Step:7 Start Installation using packstack command.
Now we are good to start the openstack installation using packstack command. Run the below command from Controller node.
[root@controller ~]# packstack --answer-file=/root/answer.txt
Once the installation is completed successfully we will get below:
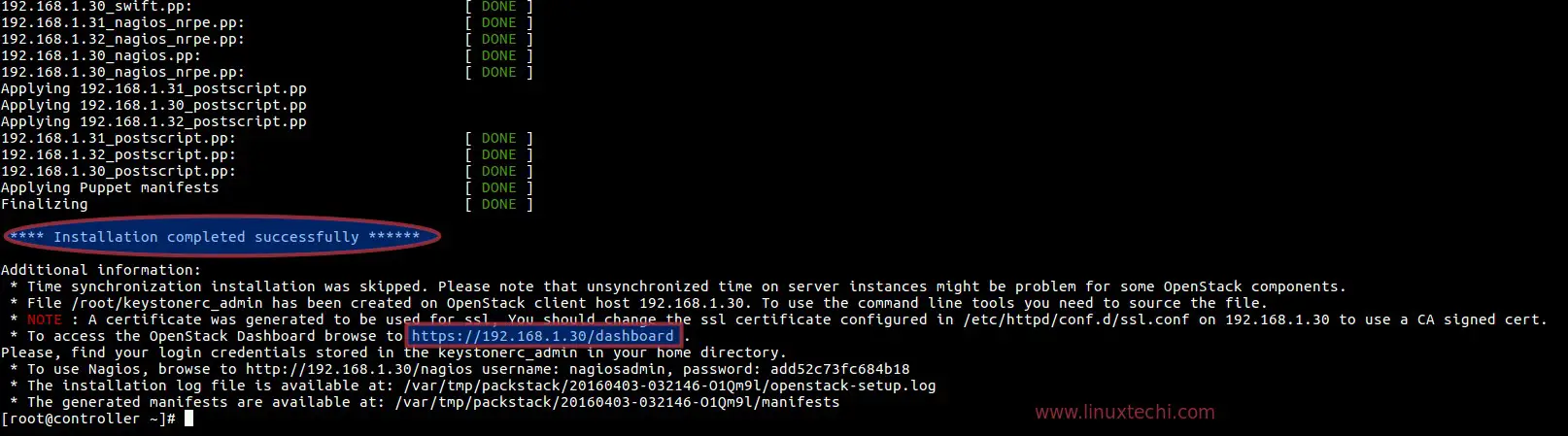
After the installation, a new interface ‘br-ex‘ will created in the network node. Add network interface (enp0s3 or eth0 or may be other name ) to the Open vSwitch ‘br-ex’ bridge as a port and assign the ip address of ‘ enp0s3’ to ‘ br-ex’
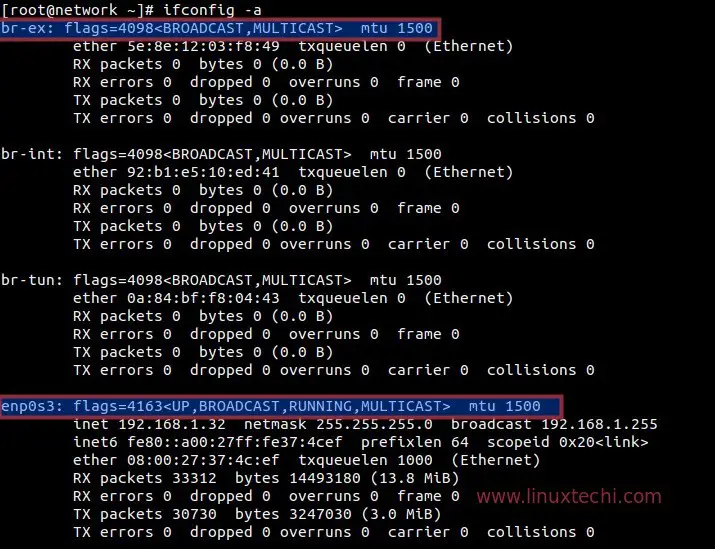
[root@network ~]# cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ [root@network network-scripts]# cp ifcfg-enp0s3 ifcfg-br-ex [root@network network-scripts]# vi ifcfg-enp0s3 DEVICE=enp0s3 HWADDR=08:00:27:37:4C:EF TYPE=OVSPort DEVICETYPE=ovs OVS_BRIDGE=br-ex ONBOOT=yes [root@network network-scripts]# vi ifcfg-br-ex DEVICE=br-ex DEVICETYPE=ovs TYPE=OVSBridge BOOTPROTO=static IPADDR=192.168.1.32 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 GATEWAY=192.168.1.1 DNS1=192.168.1.11 ONBOOT=yes
Restart the Network service using below command.
[root@network network-scripts]# systemctl restart network [root@network network-scripts]#
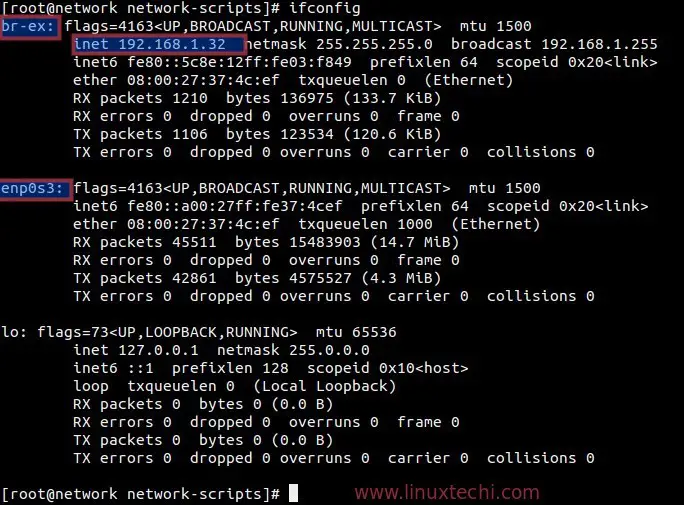
Step:8 Access Openstack Dashboard.
Now try to access the openstack dashboard from the browser using below.
https://192.168.1.30/dashboard
Use user name as ‘admin’ and password that you specify in the answer.txt file.
Click on ‘Connect’
Note : In case you are getting ‘Error: Unable to retrieve volume limit information’ in the dashboard, this can be fixed by adding the following in the cinder.conf file on the controller node.
[root@controller ~]# vi /etc/cinder/cinder.conf
....................................
[keystone_authtoken]
auth_uri = http://<Controller_IP>:5000
auth_url = http://<Controller_IP>:35357
auth_plugin = password
project_domain_id = default
user_domain_id = default
project_name = services
username = cinder
password = <Cinder_Password> {Search CONFIG_CINDER_KS_PW in answer file}
.....................................
Restart the Cinder Service.
[root@controller ~]# systemctl restart openstack-cinder-api.service [root@controller ~]# systemctl restart openstack-cinder-backup.service [root@controller ~]# systemctl restart openstack-cinder-scheduler.service [root@controller ~]# systemctl restart openstack-cinder-volume.service
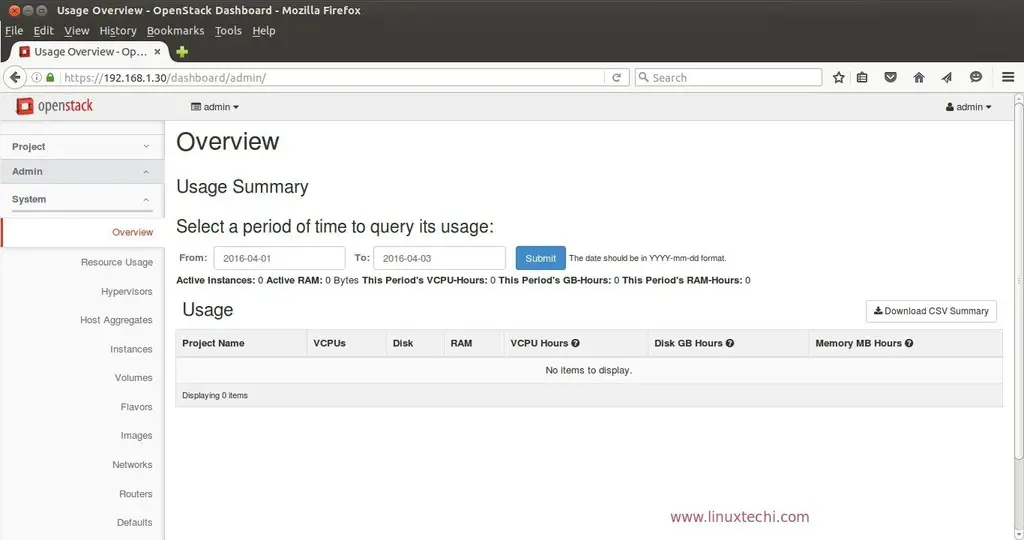
As we are able to login in the dashboard, so we can say that Installation part is completed. Now the next task is to launch an instance, for that we need to perform following tasks .
- Create Project and Users
- Assign Users to the Project.
- Create image and flavors
- Define Internal and external network
- Create Router
- Create Security Rules for Virtual Machine or instance.
To accomplish above task refer the below URL :
Reference : – https://www.rdoproject.org/install/quickstart/
Related Posts
 How to Install TeamViewer On Ubuntu 15.04
How to Install TeamViewer On Ubuntu 15.04 Installation Steps of VirtualBox on OpenSUSE 13.1 & 13.2
Installation Steps of VirtualBox on OpenSUSE 13.1 & 13.2 20 Linux Virtualization Interview Questions & Answers
20 Linux Virtualization Interview Questions & Answers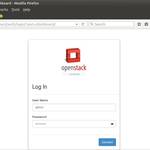 Single Node OpenStack (Liberty) Installation Steps on CentOS 7
Single Node OpenStack (Liberty) Installation Steps on CentOS 7 How to Install and use Lsyncd on CentOS 7 & RHEL 7
How to Install and use Lsyncd on CentOS 7 & RHEL 7 Install & Configure Apache Subversion (SVN) on CentOS 7
Install & Configure Apache Subversion (SVN) on CentOS 7 Linux/UNIX wget command with practical examples
Linux/UNIX wget command with practical examples
- NEXT STORYInstall Zabbix 3.0 (Monitoring Server) on CentOS 7.x / RHEL 7.x
- PREVIOUS STORY10 ‘rm’ command examples for beginners
18 Responses
Leave a Reply
Subscribe To Newsletter
Follow Us On G+
-
September 19, 2016
-
September 11, 2016
-
August 26, 2016
-
August 15, 2016
-
August 8, 2016
-
August 1, 2016
-
July 27, 2016
-
July 19, 2016






Few questions.
object storage is —containers ?
Block storage is — Volumes?
Block Storage – Cinder Service provide block storage, yes volumes are block storage
All the 3 node have internet connection and reachable from one another.
br-ex: flags=4163 mtu 1500
inet 192.168.0.130 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.0.255
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fecf:c042 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20
ether 08:00:27:cf:c0:42 txqueuelen 0 (Ethernet)
RX packets 3614 bytes 293226 (286.3 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 3369 bytes 280514 (273.9 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fecf:c042 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20
ether 08:00:27:cf:c0:42 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 11537 bytes 1609837 (1.5 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 3370 bytes 293443 (286.5 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10
loop txqueuelen 0 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 2 bytes 190 (190.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 2 bytes 190 (190.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
inet 192.168.122.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.122.255
ether 52:54:00:73:4b:e7 txqueuelen 0 (Ethernet)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
nic2 External
Compute Node: nic1 Manament
nic2 External
If I want to have more than 1 compute nodes then how can I do this ? What all changes I need to do in answer file ?
CONFIG_COMPUTE_HOSTS=’ip_address_of_new_compute_node’