How to Install PostgreSQL and phpPgAdmin on Ubuntu 16.04
https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/ubuntu-postgresql-installation/
This tutorial exists for these OS versions
- Ubuntu 15.04 (Vivid Vervet)
- Ubuntu 15.04 (Vivid Vervet)
On this page
PostgreSQL or Postgres is a powerful high-performance object-relational database management system (ORDBMS) released under a flexible BSD-style license. PostgreSQL is well suited for large databases and has many advanced features.
PostgreSQL is available for many operating systems including Linux, FreeBSD, Solaris, and Microsoft Windows.
PhpPgAdmin is a PHP-based web application for managing PostgreSQL databases. With Phppgadmin, it is easy to create a database, create a role and create tables in Postgres.
PhpPgAdmin is a PHP-based web application for managing PostgreSQL databases. With Phppgadmin, it is easy to create a database, create a role and create tables in Postgres.
This tutorial will show the installation of PostgreSQL and its web-based administration interface phpPgAdmin on Ubuntu 16.04. I will use the Ubuntu minimal server as basis for this setup.
Prerequisites
- Ubuntu Server 16.04.
- Root/Sudo access.
What we will do in this tutorial:
- Install PostgreSQL, phpPgAdmin and Apache2.
- Configure a PostgreSQL User.
- Configure Apache2.
- Configure phpPgAdmin.
- Testing.
Step 1 - Installing PostgreSQL, phpPgAdmin and Apache2
PostgreSQL and PhpPgAdmin are available in the Ubuntu repository. So you just need to install them with the apt command.
sudo apt-get -y install postgresql postgresql-contrib phppgadmin
The above command will automatically install all packages needed by PostgreSQL, like Apache, PHP etc.
Step 2 - Configure PostgreSQL user
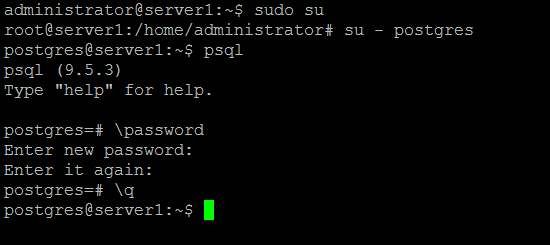
PostgreSQL uses role for user authentication and authorization, it just like Unix-Style permissions. By default, PostgreSQL creates a new user called "postgres" for basic authentication. To use PostgreSQL, you need to login to the "postgres" account, you can do that by typing:
sudo su
su - postgres
su - postgres
Now you can access the PostgreSQL prompt with the command:
psql
And then change the password for postgres role by typing:
\password postgres
ENTER YOUR PASSWORD
ENTER YOUR PASSWORD
Then enter \q to leave the psql command line.
Run the command "exit" to leave the postgres user and become root again.
exit
Step 3 - Configure Apache2
You need to configure apache for phpPgAdmin. Edit the file /etc/apache2/conf-available/phppgadmin.conf with nano by typing:
cd /etc/apache2/conf-available/
nano phppgadmin.conf
nano phppgadmin.conf
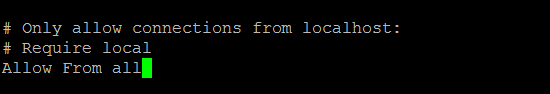
Comment out the line #Require local by adding a # in front of the line and add below the line allow from all so that you can access from your browser.
Step 4 - Configure phpPgAdmin
Edit the file /etc/phppgadmin/config.inc.php by typing :
cd /etc/phppgadmin/
nano config.inc.php
nano config.inc.php
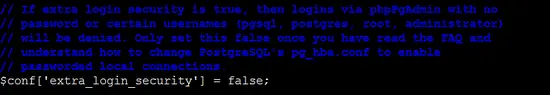
Find the line $conf['extra_login_security'] = true; and change the value to false so you can login to phpPgAdmin with user postgres.
Step 5 - Restart PostgreSQL and Apache2
systemctl restart postgresql
systemctl restart apache2
systemctl restart apache2
Step 6 - Testing
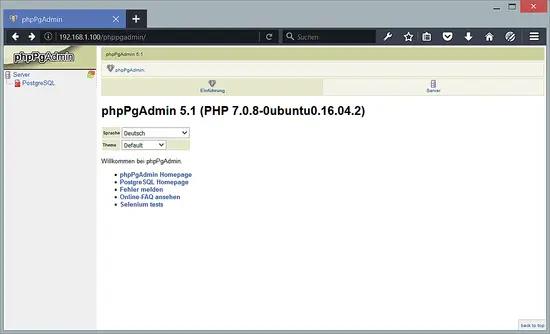
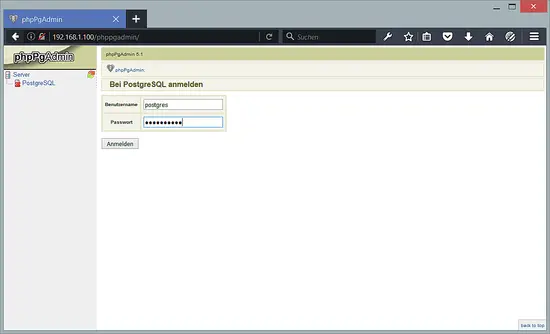
Now access phpPgAdmin with your browser http://yourip/phppgadmin/.
and then try login to with user postgres and your password.
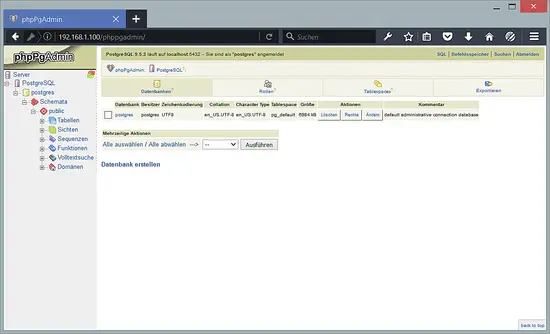
After logging in you will get this interface:
Conclusion
PostgreSQL is an advanced object-relational database management system (ORDBMS), it is Open Source and has a large and active Community. PostgreSQL provides the psql command line program as primary front-end, which can be used to enter SQL queries directly, or execute them from a file. phpPgAdmin is a web-based administration tool for PostgreSQL written in PHP that makes the administration of Postgres databases easier.
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar